Page 106 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 106
2.5. Image Processing with Optics
LCTV
CCD
Input
source xdD——
CCD Microcomputer
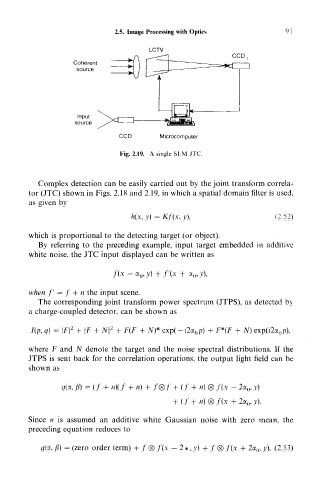
Fig. 2.19. A single SLM JTC
Complex detection can be easily carried out by the joint transform correla-
tor (JTC) shown in Figs. 2.18 and 2.19, in which a spatial domain filter is used,
as given by
h(x, y) = Kf(x, y), (2.52)
which is proportional to the detecting target (or object).
By referring to the preceding example, input target embedded in additive
white noise, the JTC input displayed can be written as
f(x - <x 0, y) + f'(x + « 0, y),
when f — f + n the input scene.
The corresponding joint transform power spectrum (JTPS), as detected by
a charge-coupled detector, can be shown as
2 2
, q) - F\ + \F + N\ + F(F + N)* F*(F + N) exp(/2« 0p).
where F and N denote the target and the noise spectral distributions. If the
JTPS is sent back for the correlation operations, the output light field can be
shown as
<7(oc, 0) = (/ + n)(f + n) + (f + n) ® f(x - 2a 0, >•)
(/ + n)(x)/(x +2a 0 ,y).
Since n is assumed an additive white Gaussian noise with zero mean, the
preceding equation reduces to
0(a, /?) = (zero order term) + / <g) f(x - 2 * , v) + / ® f(x + 2a 0, y), (2.53)