Page 378 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 378
7.1. Basic Architectures
for example, by Aa and A/?, in the Fourier plane, as given by
H(a. - Aa, /i - A/?), (7.1)
the output correlation distribution can be shown as
R(x, y) *, y) exp i — (xAa + <g) F(x, y), (7.2)
where <g) denotes the correlation operation. Thus, we see that the larger the
transversal misalignment of the Fourier-domain filter, the higher the degrada-
tion of signal detection will be.
On the other hand, JTC will not pose any major problem of the spatial-
domain filter h(x, y) transversal misalignment, since the fringe visibility of the
JTPS is independent of the filter translation. As for the longitudinal misalign-
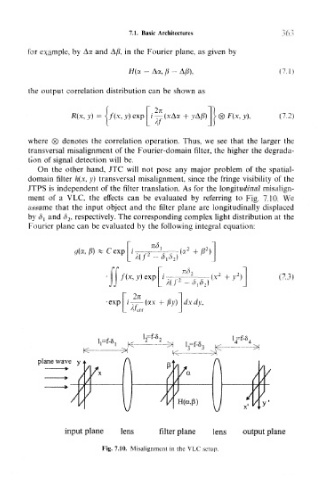
ment of a VLC, the effects can be evaluated by referring to Fig. 7.10. We
assume that the input object and the filter plane are longitudinally displaced
by <5j and <3 2, respectively. The corresponding complex light distribution at the
Fourier plane can be evaluated by the following integral equation:
g(a, ft) zz C exp
2
2
/(x, v) exp i — -5 ----- ---—(x + y ) (7.31
-
• exp i — - (ax + fiy) dx dy,
l-f-8.
4 4
plane wave yf < > < / / \ P' \ /
;
3
/ A / A
//' / / H(a,p) /,}
w \ X*
input plane lens filter plane lens output plane
Fig. 7.10. Misalignment in the VLC setup.