Page 381 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 381
366 7. Pattern Recognition with Optics
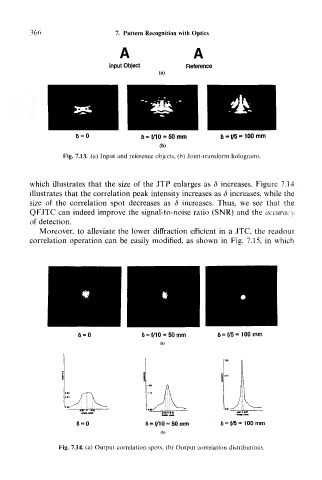
A A
Input Object Reference
(a)
6 « V5 = 100 mm
Fig. 7.13. (a) Input and reference objects, (b) Joint-transform holograms.
which illustrates that the size of the JTP enlarges as d increases. Figure 7,14
illustrates that the correlation peak intensity increases as 3 increases, while the
size of the correlation spot decreases as d increases. Thus, we see that the
QFJTC can indeed improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the accuracy
of detection.
Moreover, to alleviate the lower diffraction efficient in a JTC, the readout
correlation operation can be easily modified, as shown in Fig. 7.15, in which
6 = 0 f/5= 100mm
8 = 0 50 mm 100mm
Fig. 7.14. (a) Output correlation spots, (b) Output correlation distributions.