Page 648 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 648
63: 11. Information Display with Optics
(a ~ small). For the strong interaction regime, the situation is compounded by
another well-known fact that the diffracted light-beam profile is distorted and
hence tends to further lower the diffraction efficiency [11,14]. (Interested
readers are encouraged to explore this further.)
11.3. 3-D HOLOGRAPHIC DISPLAY
In this section, we first develop the principles of holography. We then
discuss two modern and novel electronic holographic techniques: optical
scanning holography and synthetic aperture holography. Acousto-optic modu-
lators play an essential role in both of these techniques.
11.3.1. PRINCIPLES OF HOLOGRAPHY
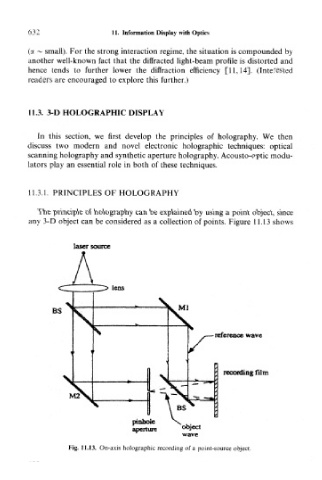
The principle of holography can be explained by using a point object, since
any 3-D object can be considered as a collection of points. Figure 11.13 shows
laser source
lens
ES
recording film
pinhde
aperture
Fig. 11.13. On-axis holographic recording of a point-source object.