Page 690 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 690
674 12. Networking with Optics
OF Gain
E • EOF Absorption
(8 3.1 • Transmission Fiber
•0
f,,
co
JQ
1
a
O
1.1
0.1
0.9 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.6
Wavelength (urn)
Level 3
I
980 nm Level 2
1480 ran
Level 1
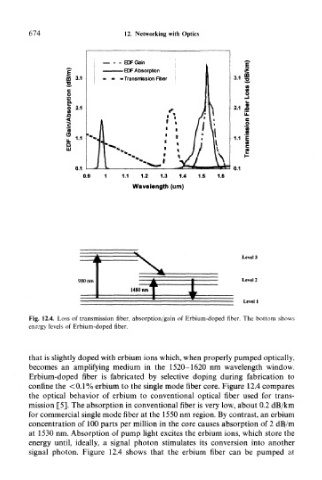
Fig. 12.4. Loss of transmission fiber, absorption/gain of Erbium-doped fiber. The bottom shows
energy levels of Erbium-doped fiber.
that is slightly doped with erbium ions which, when properly pumped optically,
becomes an amplifying medium in the 1520-1620 nm wavelength window.
Erbium-doped fiber is fabricated by selective doping during fabrication to
confine the <0.1% erbium to the single mode fiber core. Figure 12.4 compares
the optical behavior of erbium to conventional optical fiber used for trans-
mission [5]. The absorption in conventional fiber is very low, about 0.2 dB/km
for commercial single mode fiber at the 1550 nm region. By contrast, an erbium
concentration of 100 parts per million in the core causes absorption of 2 dB/m
at 1530 nm. Absorption of pump light excites the erbium ions, which store the
energy until, ideally, a signal photon stimulates its conversion into another
signal photon. Figure 12.4 shows that the erbium fiber can be pumped at