Page 107 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 107
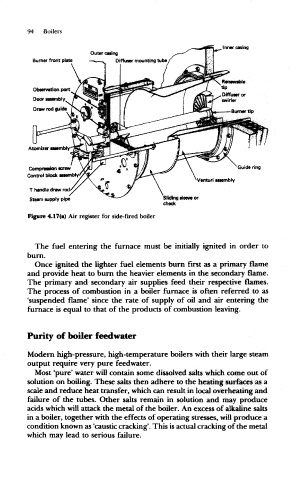
94 Boilers
Inner casing
Outer casing
Burner front plate Diffuser mounting tube.
Observation port
Door assembly
Compression screw Guide ring
Control block assembly
Venturi assembly
Sliding sleeve or
check
Figure 4.17(a) Air register for side-fired boiler
The fuel entering the furnace must be initially ignited in order to
burn.
Once ignited the lighter fuel elements burn first as a primary flame
and provide heat to burn the heavier elements in the secondary flame.
The primary and secondary air supplies feed their respective flames.
The process of combustion in a boiler furnace is often referred to as
'suspended flame' since the rate of supply of oil and air entering the
furnace is equal to that of the products of combustion leaving.
Purity of boiler feedwater
Modern high-pressure, high-temperature boilers with their large steam
output require very pure feedwater.
Most 'pure* water will contain some dissolved salts which come out of
solution on boiling. These salts then adhere to the heating surfaces as a
scale and reduce heat transfer, which can result in local overheating and
failure of the tubes. Other salts remain in solution and may produce
acids which will attack the metal of the boiler. An excess of alkaline salts
in a boiler, together with the effects of operating stresses, will produce a
condition known as 'caustic cracking'. This is actual cracking of the metal
which may lead to serious failure.