Page 87 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 87
74 Boilers
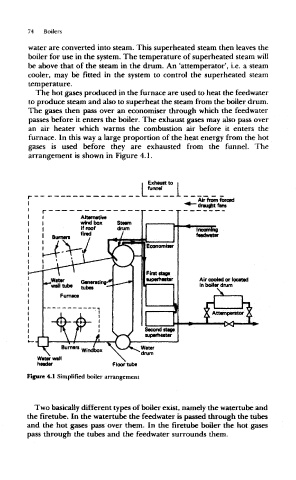
water are converted into steam. This superheated steam then leaves the
boiler for use in the system. The temperature of superheated steam will
be above that of the steam in the drum. An 'attemperator', i.e. a steam
cooler, may be fitted in the system to control the superheated steam
temperature.
The hot gases produced in the furnace are used to heat the feedwater
to produce steam and also to superheat the steam from the boiler drum.
The gases then pass over an economiser through which the feedwater
passes before it enters the boiler. The exhaust gases may also pass over
an air heater which warms the combustion air before it enters the
furnace. In this way a large proportion of the heat energy from the hot
gases is used before they are exhausted from the funnel. The
arrangement is shown in Figure 4.1.
Exhaust to
funnel
r
i Alternative
I wind box Steam
I if roof drum
Water wall
header Floor tube
Figure 4,1 Simplified boiler arrangement
Two basically different types of boiler exist, namely the watertube and
the firetube. In the watertube the feedwater is passed through the tubes
and the hot gases pass over them. In the firetube boiler the hot gases
pass through the tubes and the feedwater surrounds them.