Page 41 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 41
] 8 Chapter 1 Basic Computer Structure and the 6812
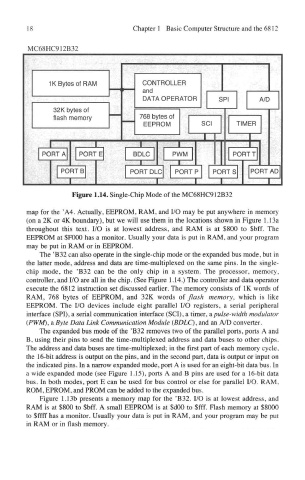
Figure 1.14. Single-Chip Mode of the MC68HC912B32
map for the 'A4. Actually, EEPROM, RAM, and I/O may be put anywhere in memory
(on a 2K or 4K boundary), but we will use them in the locations shown in Figure 1.13a
throughout this text. I/O is at lowest address, and RAM is at $800 to $bff. The
EEPROM at $FOOO has a monitor. Usually your data is put in RAM, and your program
may be put in RAM or in EEPROM.
The 'B32 can also operate in the single-chip mode or the expanded bus mode, but in
the latter mode, address and data are time-multiplexed on the same pins. In the single-
chip mode, the 'B32 can be the only chip in a system. The processor, memory,
controller, and I/O are all in the chip. (See Figure 1.14.) The controller and data operator
execute the 6812 instruction set discussed earlier. The memory consists of IK words of
RAM, 768 bytes of EEPROM, and 32K words of flash memory, which is like
EEPROM. The I/O devices include eight parallel I/O registers, a serial peripheral
interface (SPI), a serial communication interface (SCI), a timer, & pulse-width modulator
(PWM), a Byte Data Link Communication Module (BDLC), and an A/D converter.
The expanded bus mode of the 'B32 removes two of the parallel ports, ports A and
B, using their pins to send the time-multiplexed address and data buses to other chips.
The address and data buses are time-multiplexed; in the first part of each memory cycle,
the 16-bit address is output on the pins, and in the second part, data is output or input on
the indicated pins. In a narrow expanded mode, port A is used for an eight-bit data bus. In
a wide expanded mode (see Figure 1.15), ports A and B pins are used for a 16-bit data
bus. In both modes, port E can be used for bus control or else for parallel I/O. RAM.
ROM, EPROM, and PROM can be added to the expanded bus.
Figure 1.13b presents a memory map for the 'B32. I/O is at lowest address, and
RAM is at $800 to $bff. A small EEPROM is at $dOO to $fff. Flash memory at $8000
to $ffff has a monitor. Usually your data is put in RAM, and your program may be put
in RAM or in flash memory.