Page 140 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 140
SEISMIC RESOLUTION 127
The maximum vertical resolution can be increased by reducing the dominant
frequency of the seismic wavelet.
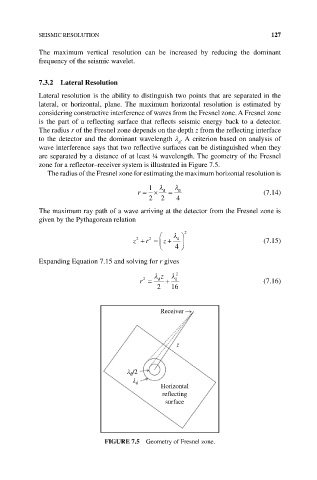
7.3.2 Lateral Resolution
Lateral resolution is the ability to distinguish two points that are separated in the
lateral, or horizontal, plane. The maximum horizontal resolution is estimated by
considering constructive interference of waves from the Fresnel zone. A Fresnel zone
is the part of a reflecting surface that reflects seismic energy back to a detector.
The radius r of the Fresnel zone depends on the depth z from the reflecting interface
to the detector and the dominant wavelength λ . A criterion based on analysis of
d
wave interference says that two reflective surfaces can be distinguished when they
are separated by a distance of at least ¼ wavelength. The geometry of the Fresnel
zone for a reflector–receiver system is illustrated in Figure 7.5.
The radius of the Fresnel zone for estimating the maximum horizontal resolution is
1 λ λ
r = × d = d (7.14)
2 2 4
The maximum ray path of a wave arriving at the detector from the Fresnel zone is
given by the Pythagorean relation
λ 2
z + r = z + d (7.15)
2
2
4
Expanding Equation 7.15 and solving for r gives
λ z λ 2
2
r = d + d (7.16)
2 16
Receiver
z
d /2
d
Horizontal
reflecting
surface
FIGuRE 7.5 Geometry of Fresnel zone.