Page 337 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 337
316 Introduction to Microfabrication
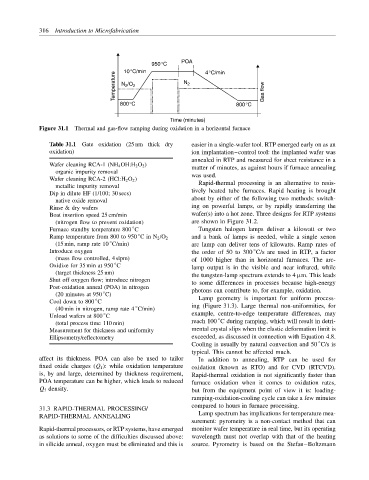
950°C POA
10°C/min 4°C/min
Temperature N 2 /O 2 N 2 Gas flow
800°C 800°C
Time (minutes)
Figure 31.1 Thermal and gas-flow ramping during oxidation in a horizontal furnace
Table 31.1 Gate oxidation (25 nm thick dry easier in a single-wafer tool. RTP emerged early on as an
oxidation) ion implantation–control tool: the implanted wafer was
annealed in RTP and measured for sheet resistance in a
Wafer cleaning RCA-1 (NH 4 OH:H 2 O 2 )
matter of minutes, as against hours if furnace annealing
organic impurity removal
Wafer cleaning RCA-2 (HCl:H 2 O 2 ) was used.
metallic impurity removal Rapid-thermal processing is an alternative to resis-
Dip in dilute HF (1/100; 30 secs) tively heated tube furnaces. Rapid heating is brought
native oxide removal about by either of the following two methods: switch-
Rinse & dry wafers ing on powerful lamps, or by rapidly transferring the
Boat insertion speed 25 cm/min wafer(s) into a hot zone. Three designs for RTP systems
(nitrogen flow to prevent oxidation) are shown in Figure 31.2.
◦
Furnace standby temperature 800 C Tungsten halogen lamps deliver a kilowatt or two
◦
Ramp temperature from 800 to 950 C in N 2 /O 2 and a bank of lamps is needed, while a single xenon
(15 min, ramp rate 10 C/min) arc lamp can deliver tens of kilowatts. Ramp rates of
◦
Introduce oxygen the order of 50 to 300 C/s are used in RTP, a factor
◦
(mass flow controlled, 4 slpm) of 1000 higher than in horizontal furnaces. The arc-
◦
Oxidize for 35 min at 950 C lamp output is in the visible and near infrared, while
(target thickness 25 nm) the tungsten-lamp spectrum extends to 4 µm. This leads
Shut off oxygen flow; introduce nitrogen to some differences in processes because high-energy
Post-oxidation anneal (POA) in nitrogen photons can contribute to, for example, oxidation.
(20 minutes at 950 C)
◦
◦
Cool down to 800 C Lamp geometry is important for uniform process-
◦
(40 min in nitrogen, ramp rate 4 C/min) ing (Figure 31.3). Large thermal non-uniformities, for
◦
Unload wafers at 800 C example, centre-to-edge temperature differences, may
◦
(total process time 110 min) reach 100 C during ramping, which will result in detri-
Measurement for thickness and uniformity mental crystal slips when the elastic deformation limit is
Ellipsometry/reflectometry exceeded, as discussed in connection with Equation 4.8.
◦
Cooling is usually by natural convection and 50 C/s is
typical. This cannot be affected much.
affect its thickness. POA can also be used to tailor In addition to annealing, RTP can be used for
fixed oxide charges (Q f ): while oxidation temperature oxidation (known as RTO) and for CVD (RTCVD).
is, by and large, determined by thickness requirement, Rapid-thermal oxidation is not significantly faster than
POA temperature can be higher, which leads to reduced furnace oxidation when it comes to oxidation rates,
Q f density. but from the equipment point of view it is: loading-
ramping-oxidation-cooling cycle can take a few minutes
compared to hours in furnace processing.
31.3 RAPID-THERMAL PROCESSING/
RAPID-THERMAL ANNEALING Lamp spectrum has implications for temperature mea-
surement: pyrometry is a non-contact method that can
Rapid-thermal processors, or RTP systems, have emerged monitor wafer temperature in real time, but its operating
as solutions to some of the difficulties discussed above: wavelength must not overlap with that of the heating
in silicide anneal, oxygen must be eliminated and this is source. Pyrometry is based on the Stefan–Boltzmann