Page 338 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 338
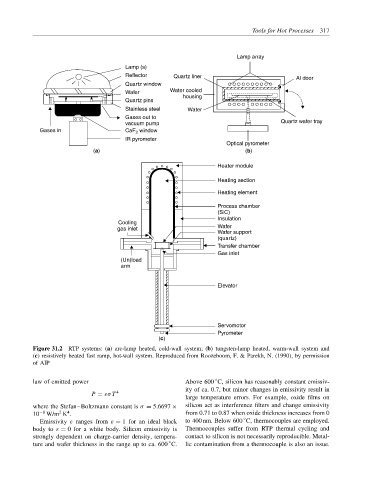
Tools for Hot Processes 317
Lamp array
Lamp (s)
Reflector Quartz liner Al door
Quartz window
Wafer Water cooled
housing
Quartz pins
Stainless steel Water
Gases out to
vacuum pump Quartz wafer tray
Gases in CaF 2 window
IR pyrometer
Optical pyrometer
(a) (b)
Heater module
Heating section
Heating element
Process chamber
(SiC)
Insulation
Cooling
gas inlet Wafer
Wafer support
(quartz)
Transfer chamber
Gas inlet
(Un)load
arm
Elevator
Servomotor
Pyrometer
(c)
Figure 31.2 RTP systems: (a) arc-lamp heated, cold-wall system; (b) tungsten-lamp heated, warm-wall system and
(c) resistively heated fast ramp, hot-wall system. Reproduced from Roozeboom, F. & Parekh, N. (1990), by permission
of AIP
law of emitted power Above 600 C, silicon has reasonably constant emissiv-
◦
ity of ca. 0.7, but minor changes in emissivity result in
4
P = εσT
large temperature errors. For example, oxide films on
where the Stefan–Boltzmann constant is σ = 5.6697 × silicon act as interference filters and change emissivity
2
4
10 −8 W/m K . from 0.71 to 0.87 when oxide thickness increases from 0
◦
Emissivity ε ranges from ε = 1 for an ideal black to 400 nm. Below 600 C, thermocouples are employed.
body to ε = 0 for a white body. Silicon emissivity is Thermocouples suffer from RTP thermal cycling and
strongly dependent on charge-carrier density, tempera- contact to silicon is not necessarily reproducible. Metal-
ture and wafer thickness in the range up to ca. 600 C. lic contamination from a thermocouple is also an issue.
◦