Page 28 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 28
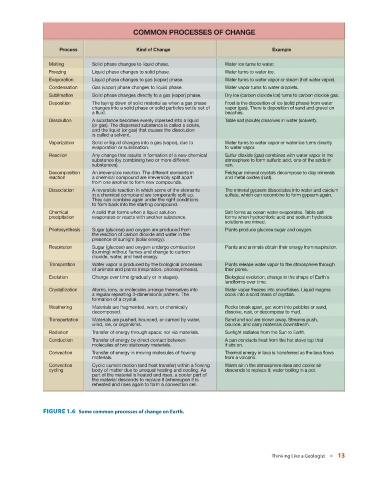
COMMON PROCESSES OF CHANGE
Process Kind of Change Example
Melting Solid phase changes to liquid phase. Water ice turns to water.
Freezing Liquid phase changes to solid phase. Water turns to water ice.
Evaporation Liquid phase changes to gas (vapor) phase. Water turns to water vapor or steam (hot water vapor).
Condensation Gas (vapor) phase changes to liquid phase. Water vapor turns to water droplets.
Sublimation Solid phase changes directly to a gas (vapor) phase. Dry ice (carbon dioxide ice) turns to carbon dioxide gas.
Deposition The laying down of solid material as when a gas phase Frost is the deposition of ice (solid phase) from water
changes into a solid phase or solid particles settle out of vapor (gas). There is deposition of sand and gravel on
a fluid. beaches.
Dissolution A substance becomes evenly dipersed into a liquid Table salt (solute) dissolves in water (solvent).
(or gas). The dispersed substance is called a solute,
and the liquid (or gas) that causes the dissolution
is called a solvent.
Vaporization Solid or liquid changes into a gas (vapor), due to Water turns to water vapor or water ice turns directly
evaporation or sublimation. to water vapor.
Reaction Any change that results in formation of a new chemical Sulfur dioxide (gas) combines with water vapor in the
substance (by combining two or more different atmosphere to form sulfuric acid, one of the acids in
substances). rain.
Decomposition An irreversible reaction. The different elements in Feldspar mineral crystals decompose to clay minerals
reaction a chemical compound are irreversibly split apart and metal oxides (rust).
from one another to form new compounds.
Dissociation A reversible reaction in which some of the elements The mineral gypsum dissociates into water and calcium
in a chemical compound are temporarily split up. sulfate, which can recombine to form gypsum again.
They can combine again under the right conditions
to form back into the starting compound.
Chemical A solid that forms when a liquid solution Salt forms as ocean water evaporates. Table salt
precipitation evaporates or reacts with another substance. forms when hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
solutions are mixed.
Photosynthesis Sugar (glucose) and oxygen are produced from Plants produce glucose sugar and oxygen.
the reaction of carbon dioxide and water in the
presence of sunlight (solar energy).
Respiration Sugar (glucose) and oxygen undergo combustion Plants and animals obtain their energy from respiration.
(burning) without flames and change to carbon
dioxide, water, and heat energy.
Transpiration Water vapor is produced by the biological processes Plants release water vapor to the atmosphere through
of animals and plants (respiration, photosynthesis). their pores.
Evolution Change over time (gradually or in stages). Biological evolution, change in the shape of Earth's
landforms over time.
Crystallization Atoms, ions, or molecules arrange themselves into Water vapor freezes into snowflakes. Liquid magma
a regular repeating 3-dimensional pattern. The cools into a solid mass of crystals.
formation of a crystal.
Weathering Materials are fragmented, worn, or chemically Rocks break apart, get worn into pebbles or sand,
decomposed. dissolve, rust, or decompose to mud.
Transportation Materials are pushed, bounced, or carried by water, Sand and soil are blown away. Streams push,
wind, ice, or organisms. bounce, and carry materials downstream.
Radiation Transfer of energy through space; not via materials. Sunlight radiates from the Sun to Earth.
Conduction Transfer of energy by direct contact between A pan conducts heat from the hot stove top that
molecules of two stationary materials. it sits on.
Convection Transfer of energy in moving molecules of flowing Thermal energy in lava is transferred as the lava flows
materials. from a volcano.
Convection Cyclic current motion (and heat transfer) within a flowing Warm air in the atmosphere rises and cooler air
cycling body of matter due to unequal heating and cooling. As descends to replace it; water boiling in a pot.
part of the material is heated and rises, a cooler part of
the material descends to replace it (whereupon it is
reheated and rises again to form a convection cell.
FIGURE 1.6 Some common processes of change on Earth.
Thinking Like a Geologist ■ 13