Page 366 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 366
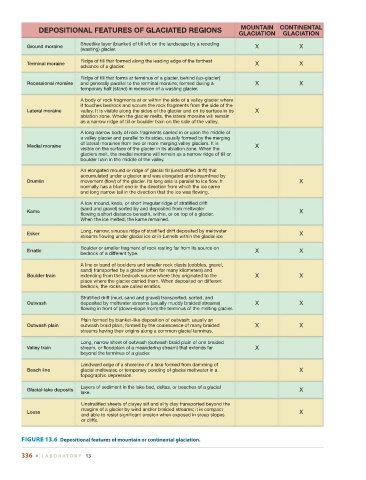
MOUNTAIN CONTINENTAL
DEPOSITIONAL FEATURES OF GLACIATED REGIONS
GLACIATION GLACIATION
Sheetlike layer (blanket) of till left on the landscape by a receding
Ground moraine X X
(wasting) glacier.
Ridge of till that formed along the leading edge of the farthest
Terminal moraine X X
advance of a glacier.
Ridge of till that forms at terminus of a glacier, behind (up-glacier)
Recessional moraine and generally parallel to the terminal moraine; formed during a X X
temporary halt (stand) in recession of a wasting glacier.
A body of rock fragments at or within the side of a valley glacier where
it touches bedrock and scours the rock fragments from the side of the
Lateral moraine valley. It is visible along the sides of the glacier and on its surface in its X
ablation zone. When the glacier melts, the lateral moraine will remain
as a narrow ridge of till or boulder train on the side of the valley.
A long narrow body of rock fragments carried in or upon the middle of
a valley glacier and parallel to its sides, usually formed by the merging
of lateral moraines from two or more merging valley glaciers. It is
Medial moraine X
visible on the surface of the glacier in its ablation zone. When the
glaciers melt, the medial moraine will remain as a narrow ridge of till or
boulder train in the middle of the valley.
An elongated mound or ridge of glacial till (unstratified drift) that
accumulated under a glacier and was elongated and streamlined by
Drumlin movement (flow) of the glacier. Its long axis is parallel to ice flow. It X
normally has a blunt end in the direction from which the ice came
and long narrow tail in the direction that the ice was flowing.
A low mound, knob, or short irregular ridge of stratified drift
(sand and gravel) sorted by and deposited from meltwater
Kame X
flowing a short distance beneath, within, or on top of a glacier.
When the ice melted, the kame remained.
Long, narrow, sinuous ridge of stratified drift deposited by meltwater
Esker X
streams flowing under glacial ice or in tunnels within the glacial ice
Boulder or smaller fragment of rock resting far from its source on
Erratic X X
bedrock of a different type.
A line or band of boulders and smaller rock clasts (cobbles, gravel,
sand) transported by a glacier (often for many kilometers) and
Boulder train extending from the bedrock source where they originated to the X X
place where the glacier carried them. When deposited on different
bedrock, the rocks are called erratics.
Stratified drift (mud, sand and gravel) transported, sorted, and
Outwash deposited by meltwater streams (usually muddy braided streams) X X
flowing in front of (down-slope from) the terminus of the melting glacier.
Plain formed by blanket-like deposition of outwash; usually an
Outwash plain outwash braid plain, formed by the coalescence of many braided X X
streams having their origins along a common glacial terminus.
Long, narrow sheet of outwash (outwash braid plain of one braided
Valley train stream, or floodplain of a meandering stream) that extends far X
beyond the terminus of a glacier.
Landward edge of a shoreline of a lake formed from damming of
Beach line glacial meltwater, or temporary ponding of glacial meltwater in a X
topographic depression.
Layers of sediment in the lake bed, deltas, or beaches of a glacial
Glacial-lake deposits X
lake.
Unstratified sheets of clayey silt and silty clay transported beyond the
margins of a glacier by wind and/or braided streams; it is compact
Loess X
and able to resist significant erosion when exposed in steep slopes
or cliffs.
FIGURE 13.6 Depositional features of mountain or continental glaciation.
336 ■ L ABOR ATORY 13