Page 410 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 410
Submergent vs. Emergent (at the mouth of the Mississippi River) is emergent
(progradational)—building out into the water. This is
Coastlines because of the vast supply of sediment being carried there
Over decades of time, geologists characterize coastlines and deposited from the Mississippi River.
as submergent (retrogradational) or emergent FIGURES 15.2 and 15.3 illustrate some features of
(progradational): in one of two ways: emergent and submergent shorelines that you will need to
identify in FIGURE 15.4 , 15.5 , and 15.6 Study these features
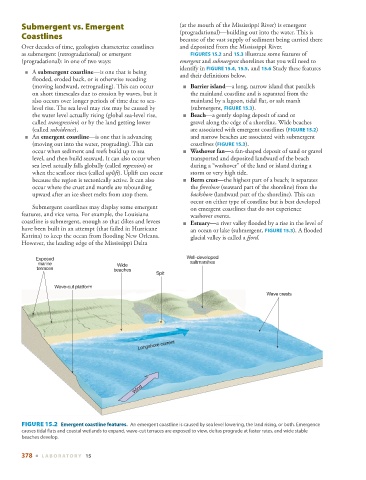
■ A submergent coastline —is one that is being and their definitions below.
flooded, eroded back, or is otherwise receding
(moving landward, retrograding). This can occur ■ Barrier island —a long, narrow island that parallels
on short timescales due to erosion by waves, but it the mainland coastline and is separated from the
also occurs over longer periods of time due to sea- mainland by a lagoon, tidal flat, or salt marsh
level rise. The sea level may rise may be caused by (submergent, FIGURE 15.3 ).
the water level actually rising (global sea-level rise, ■ Beach —a gently sloping deposit of sand or
called transgression ) or by the land getting lower gravel along the edge of a shoreline. Wide beaches
(called subsidence ). are associated with emergent coastlines ( FIGURE 15.2 )
■ An emergent coastline —is one that is advancing and narrow beaches are associated with submergent
(moving out into the water, prograding). This can coastlines ( FIGURE 15.3 ).
occur when sediment and reefs build up to sea ■ Washover fan —a fan-shaped deposit of sand or gravel
level, and then build seaward. It can also occur when transported and deposited landward of the beach
sea level actually falls globally (called regression ) or during a “washover” of the land or island during a
when the seafloor rises (called uplift ). Uplift can occur storm or very high tide.
because the region is tectonically active. It can also ■ Berm crest —the highest part of a beach; it separates
occur where the crust and mantle are rebounding the foreshore (seaward part of the shoreline) from the
upward after an ice sheet melts from atop them. backshore (landward part of the shoreline). This can
occur on either type of coastline but is best developed
Submergent coastlines may display some emergent on emergent coastlines that do not experience
features, and vice versa. For example, the Louisiana washover events.
coastline is submergent, enough so that dikes and levees ■ Estuary —a river valley flooded by a rise in the level of
have been built in an attempt (that failed in Hurricane an ocean or lake (submergent, FIGURE 15.3 ). A flooded
Katrina) to keep the ocean from flooding New Orleans. glacial valley is called a fjord .
However, the leading edge of the Mississippi Delta
Exposed Well-developed
marine Wide saltmarshes
terraces beaches
Spit
Wave-cut platform
Wave crests
Longshore current
Wind
FIGURE 15.2 Emergent coastline features. An emergent coastline is caused by sea level lowering, the land rising, or both. Emergence
causes tidal flats and coastal wetlands to expand, wave-cut terraces are exposed to view, deltas prograde at faster rates, and wide stable
beaches develop.
378 ■ L ABOR ATORY 15