Page 57 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 57
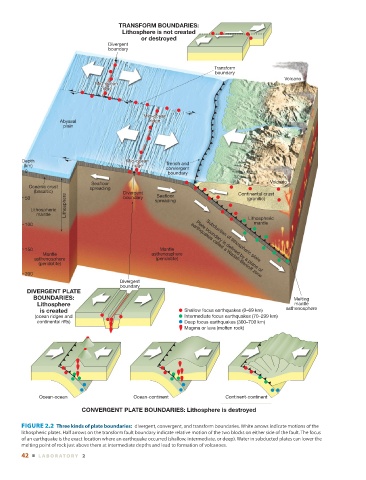
TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES:
Lithosphere is not created
or destroyed
Divergent
boundary
Transform
boundary
Volcano
Mid-ocean
Mid-ocean
Mid-ocean
ridge
ridge
ridge
Mid-ocean
Mid-ocean
Mid-ocean
ridge
ridge
Abyssal ridge
plain ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
Mid-ocean
Mid-ocean
Depth Mid-ocean Trench and
ridge
ridge
(km) ridge convergent
0 boundary
Seafloor Volcano
Oceanic crust spreading
(basaltic) Divergent Continental crust
Lithosphere
Seafloor
50 boundary spreading (granitic)
Lithospheric
mantle
Lithospheric
mantle
100 ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
150 Mantle earthquakes called a Wadati-Benioff zone
Mantle asthenosphere
asthenosphere (peridotite)
Subduction of lithospheric plate
(peridotite)
Plate boundary is defined by a plane of
200
Divergent
boundary
DIVERGENT PLATE
BOUNDARIES: Melting
Lithosphere mantle
asthenosphere
is created Shallow focus earthquakes (0–69 km)
(ocean ridges and Intermediate focus earthquakes (70–299 km)
continental rifts) Deep focus earthquakes (300–700 km)
Magma or lava (molten rock) ▲
▲
▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
▲ ▲ ▲
▲ ▲ ▲
▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲ ▲
Ocean-ocean Ocean-continent Continent-continent
CONVERGENT PLATE BOUNDARIES: Lithosphere is destroyed
FIGURE 2.2 Three kinds of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries. White arrows indicate motions of the
lithospheric plates. Half arrows on the transform fault boundary indicate relative motion of the two blocks on either side of the fault. The focus
of an earthquake is the exact location where an earthquake occurred (shallow, intermediate, or deep). Water in subducted plates can lower the
melting point of rock just above them at intermediate depths and lead to formation of volcanoes.
42 ■ L ABOR ATORY 2