Page 60 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 60
time series graph. You will need to combine the latitude What Causes Plate Tectonics?
and longitude data to determine the overall direction
and rate of plate motion for the years that the data were Recall that geoscientists have historically tried to under-
collected. See FIGURE 2.3 . stand the cause of Earth’s oceans, mountains, and global
tectonics by questioning if Earth could be shrinking,
expanding, or staying the same in size. This question can
ACTIVITY be evaluated by studying Earth’s natural forces and faults
in relation to those that you might predict to occur if the
2.2 Is Plate Tectonics Caused by size of Earth were changing. By comparing your predic-
a Change in Earth’s Size? tions to observations of the kinds of strains and faults
actually observed, it is possible to determine if Earth’s
THINK | size is changing and infer whether a change in Earth’s size
could cause plate tectonics.
About It What causes plate tectonics?
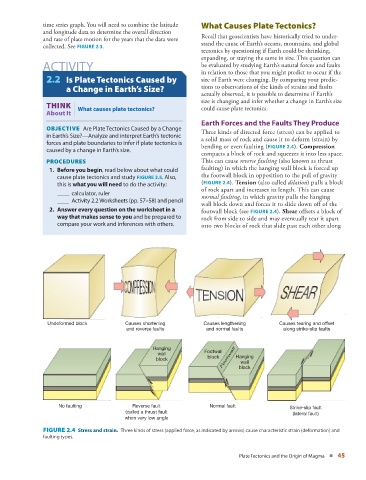
Earth Forces and the Faults They Produce
OBJECTIVE Are Plate Tectonics Caused by a Change
Three kinds of directed force (stress) can be applied to
in Earth’s Size?—Analyze and interpret Earth’s tectonic
a solid mass of rock and cause it to deform (strain) by
forces and plate boundaries to infer if plate tectonics is
bending or even faulting ( FIGURE 2.4 ). Compression
caused by a change in Earth’s size.
compacts a block of rock and squeezes it into less space.
PROCEDURES This can cause reverse faulting (also known as thrust
1. Before you begin , read below about what could faulting) in which the hanging wall block is forced up
cause plate tectonics and study FIGURE 2.5 . Also, the footwall block in opposition to the pull of gravity
this is what you will need to do the activity: ( FIGURE 2.4 ). Tension (also called dilation ) pulls a block
of rock apart and increases its length. This can cause
____ calculator, ruler
normal faulting , in which gravity pulls the hanging
____ Activity 2.2 Worksheets (pp. 57 – 58 ) and pencil
wall block down and forces it to slide down off of the
2. Answer every question on the worksheet in a footwall block (see FIGURE 2.4 ). Shear o ffsets a block of
way that makes sense to you and be prepared to rock from side to side and may eventually tear it apart
compare your work and inferences with others. into two blocks of rock that slide past each other along
Undeformed block Causes shortening Causes lengthening Causes tearing and offset
and reverse faults and normal faults along strike-slip faults
Hanging
wall Footwall
block block Footwall Hanging
wall
block
No faulting Reverse fault Normal fault Strike-slip fault
(called a thrust fault (lateral fault)
when very low angle
FIGURE 2.4 Stress and strain. Three kinds of stress (applied force, as indicated by arrows) cause characteristic strain (deformation) and
faulting types.
Plate Tectonics and the Origin of Magma ■ 45