Page 59 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 59
HOW TO PLOT AN ABSOLUTE PLATE MOTION VECTOR FROM NASA GPS TIME-SERIES
AND CALCULATE VELOCITY OF THE PLATE MOTION
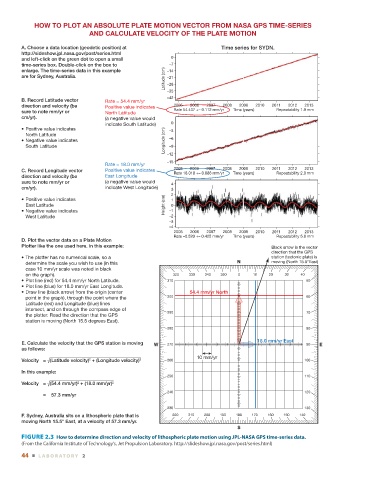
A. Choose a data location (geodetic position) at Time series for SYDN.
http://sideshow.jpl.nasa.gov/post/series.html
and left-click on the green dot to open a small 0
time-series box. Double-click on the box to –7
Latitude (cm) –28
enlarge. The time-series data in this example –14
are for Sydney, Australia. –21
–35
–42
B. Record Latitude vector Rate = 54.4 mm/yr
direction and velocity (be Positive value indicates 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
sure to note mm/yr or North Latitude Rate 54.437 +– 0.112 mm/yr Time (years) Repeatability 1.9 mm
cm/yr). (a negative value would
indicate South Latitude) 0
• Positive value indicates –3
North Latitude
• Negative value indicates Longitude (cm) –6
South Latitude –9
–12
–15
Rate = 18.0 mm/yr
2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
C. Record Longitude vector Positive value indicates Rate 18.018 +– 0.088 mm/yr Time (years) Repeatability 2.0 mm
direction and velocity (be East Longitude
sure to note mm/yr or (a negative value would 4
cm/yr). indicate West Longitude) 3
• Positive value indicates 2 1
East Latitude Height (cm) 0
• Negative value indicates –1
West Latitude –2
–3
–4
2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Rate –0.520 +– 0.425 mm/yr Time (years) Repeatability 5.8 mm
D. Plot the vector data on a Plate Motion
Plotter like the one used here. In this example: Black arrow is the vector
direction that the GPS
• The plotter has no numerical scale, so a station (tectonic plate) is
determine the scale you wish to use (in this N moving (North 15.5°East)
case 10 mm/yr scale was noted in black
on the graph). 320 330 340 350 0 10 20 30 40
• Plot line (red) for 54.4 mm/yr North Latitude. 310 50
• Plot line (blue) for 18.0 mm/yr East Longitude.
• Draw line (black arrow) from the origin (center 54.4 mm/yr North
point in the graph), through the point where the 300 60
Latitude (red) and Longitude (blue) lines
intersect, and on through the compass edge of
290 70
the plotter. Read the direction that the GPS
station is moving (North 15.5 degrees East).
280 80
18.0 mm/yr East
E. Calculate the velocity that the GPS station is moving W 270 90 E
as follows:
10 mm/yr
Velocity = √(Latitude velocity) + (Longitude velocity) 2 260 100
2
In this example:
250 110
2
Velocity = √(54.4 mm/yr) + (18.0 mm/yr) 2
240 120
= 57.3 mm/yr
230 130
F. Sydney, Australia sits on a lithospheric plate that is 220 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140
moving North 15.5° East, at a velocity of 57.3 mm/yr.
S
FIGURE 2.3 How to determine direction and velocity of lithospheric plate motion using JPL-NASA GPS time-series data.
(From the California Institute of Technology’s, Jet Propulsion Laboratory. http://slideshow.jpl.nasa.gov/post/series.html)
44 ■ L ABOR ATORY 2