Page 149 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 149
136 S. H. Gheewala
for example, greenhouse gases are aggregated into global warming potential
represented in terms of kg CO 2 eq instead of evaluating the final damage due to
climate change. The midpoint approach reduces the uncertainty introduced from
complex modeling approaches as well as forecasting and effect modeling
(Blottnitz and Curran 2007). Similar to the case for global warming, the other
impact categories of interest are acidification (kg SO 2 eq), eutrophication
3-
(kg PO 4 eq), and human toxicity (kg 1,4 DCBeq).
5.1 Ethanol from Cassava
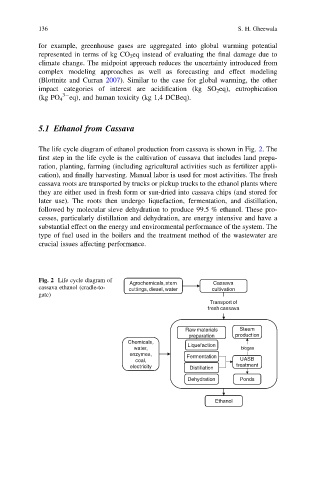
The life cycle diagram of ethanol production from cassava is shown in Fig. 2. The
first step in the life cycle is the cultivation of cassava that includes land prepa-
ration, planting, farming (including agricultural activities such as fertilizer appli-
cation), and finally harvesting. Manual labor is used for most activities. The fresh
cassava roots are transported by trucks or pickup trucks to the ethanol plants where
they are either used in fresh form or sun-dried into cassava chips (and stored for
later use). The roots then undergo liquefaction, fermentation, and distillation,
followed by molecular sieve dehydration to produce 99.5 % ethanol. These pro-
cesses, particularly distillation and dehydration, are energy intensive and have a
substantial effect on the energy and environmental performance of the system. The
type of fuel used in the boilers and the treatment method of the wastewater are
crucial issues affecting performance.
Fig. 2 Life cycle diagram of
Agrochemicals, stem Cassava
cassava ethanol (cradle-to- cuttings, diesel, water cultivation
gate)
Transport of
fresh cassava
Raw materials Steam
preparation production
Chemicals, Liquefaction
water, biogas
enzymes, Fermentation
coal, UASB
electricity Distillation treatment
Dehydration Ponds
Ethanol