Page 121 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 121
Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol and biobutanol 95
Hemicellulose
hydrolizate Solid residue:
and pretreated lignine
lignocellulosic
biomass microorganisms
Simultaneous
biomass
saccharification
and Cofermentation
Separation
Enzyme hydrolysis
Hydrolytic and
enzymes hexose and pentose Ethanol
fermentation
bioreactor
Hexose and
pentose
fermenting
microorganisms
(yeast)
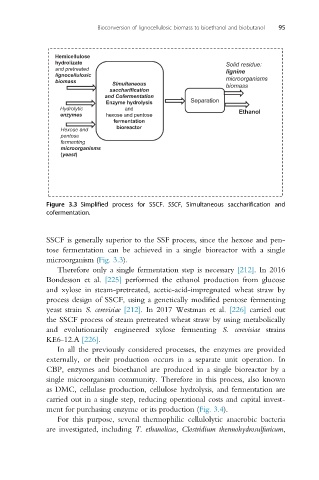
Figure 3.3 Simplified process for SSCF. SSCF, Simultaneous saccharification and
cofermentation.
SSCF is generally superior to the SSF process, since the hexose and pen-
tose fermentation can be achieved in a single bioreactor with a single
microorganism (Fig. 3.3).
Therefore only a single fermentation step is necessary [212]. In 2016
Bondesson et al. [225] performed the ethanol production from glucose
and xylose in steam-pretreated, acetic-acid-impregnated wheat straw by
process design of SSCF, using a genetically modified pentose fermenting
yeast strain S. cerevisiae [212]. In 2017 Westman et al. [226] carried out
the SSCF process of steam pretreated wheat straw by using metabolically
and evolutionarily engineered xylose fermenting S. cerevisiae strains
KE6-12.A [226].
In all the previously considered processes, the enzymes are provided
externally, or their production occurs in a separate unit operation. In
CBP, enzymes and bioethanol are produced in a single bioreactor by a
single microorganism community. Therefore in this process, also known
as DMC, cellulase production, cellulose hydrolysis, and fermentation are
carried out in a single step, reducing operational costs and capital invest-
ment for purchasing enzyme or its production (Fig. 3.4).
For this purpose, several thermophilic cellulolytic anaerobic bacteria
are investigated, including T. ethanolicus, Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum,