Page 211 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 211
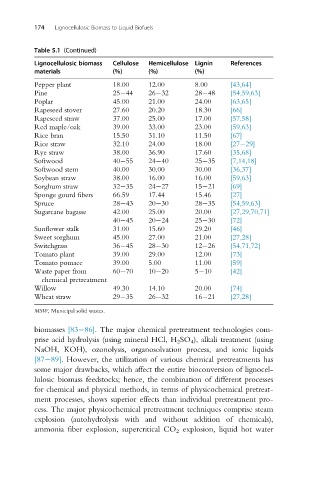
174 Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
Table 5.1 (Continued)
Lignocellulosic biomass Cellulose Hemicellulose Lignin References
materials (%) (%) (%)
Pepper plant 18.00 12.00 8.00 [43,64]
Pine 25 44 26 32 28 48 [54,59,63]
Poplar 45.00 21.00 24.00 [63,65]
Rapeseed stover 27.60 20.20 18.30 [66]
Rapeseed straw 37.00 25.00 17.00 [57,58]
Red maple/oak 39.00 33.00 23.00 [59,63]
Rice bran 15.50 31.10 11.50 [67]
Rice straw 32.10 24.00 18.00 [27 29]
Rye straw 38.00 36.90 17.60 [35,68]
Softwood 40 55 24 40 25 35 [7,14,18]
Softwood stem 40.00 30.00 30.00 [36,37]
Soybean straw 38.00 16.00 16.00 [59,63]
Sorghum straw 32 35 24 27 15 21 [69]
Sponge gourd fibers 66.59 17.44 15.46 [27]
Spruce 28 43 20 30 28 35 [54,59,63]
Sugarcane bagasse 42.00 25.00 20.00 [27,29,70,71]
40 45 20 24 25 30 [72]
Sunflower stalk 31.00 15.60 29.20 [46]
Sweet sorghum 45.00 27.00 21.00 [27,28]
Switchgrass 36 45 28 30 12 26 [54,71,72]
Tomato plant 39.00 29.00 12.00 [73]
Tomato pomace 39.00 5.00 11.00 [59]
Waste paper from 60 70 10 20 5 10 [42]
chemical pretreatment
Willow 49.30 14.10 20.00 [74]
Wheat straw 29 35 26 32 16 21 [27,28]
MSW, Municipal solid wastes.
biomasses [83 86]. The major chemical pretreatment technologies com-
prise acid hydrolysis (using mineral HCl, H 2 SO 4 ), alkali treatment (using
NaOH, KOH), ozonolysis, organosolvation process, and ionic liquids
[87 89]. However, the utilization of various chemical pretreatments has
some major drawbacks, which affect the entire bioconversion of lignocel-
lulosic biomass feedstocks; hence, the combination of different processes
for chemical and physical methods, in terms of physicochemical pretreat-
ment processes, shows superior effects than individual pretreatment pro-
cess. The major physicochemical pretreatment techniques comprise steam
explosion (autohydrolysis with and without addition of chemicals),
ammonia fiber explosion, supercritical CO 2 explosion, liquid hot water