Page 266 - Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
P. 266
222 Lignocellulosic Biomass to Liquid Biofuels
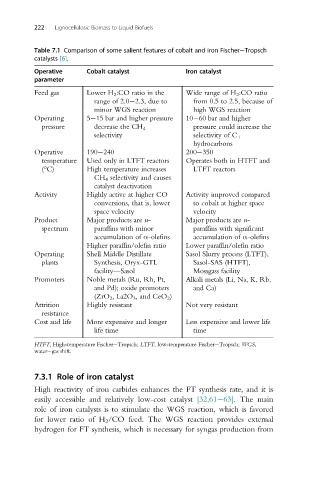
Table 7.1 Comparison of some salient features of cobalt and iron Fischer Tropsch
catalysts [6].
Operative Cobalt catalyst Iron catalyst
parameter
Feed gas Lower H 2 :CO ratio in the Wide range of H 2 :CO ratio
range of 2.0 2.3, due to from 0.5 to 2.5, because of
minor WGS reaction high WGS reaction
Operating 5 15 bar and higher pressure 10 60 bar and higher
pressure decrease the CH 4 pressure could increase the
selectivity selectivity of C 1
hydrocarbons
Operative 190 240 200 350
temperature Used only in LTFT reactors Operates both in HTFT and
(°C) High temperature increases LTFT reactors
CH 4 selectivity and causes
catalyst deactivation
Activity Highly active at higher CO Activity improved compared
conversions, that is, lower to cobalt at higher space
space velocity velocity
Product Major products are n- Major products are n-
spectrum paraffins with minor paraffins with significant
accumulation of α-olefins accumulation of α-olefins
Higher paraffin/olefin ratio Lower paraffin/olefin ratio
Operating Shell Middle Distillate Sasol Slurry process (LTFT),
plants Synthesis, Oryx-GTL Sasol-SAS (HTFT),
facility—Sasol Mossgass facility
Promoters Noble metals (Ru, Rh, Pt, Alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb,
and Pd); oxide promoters and Ca)
(ZrO 2 , La2O 3 , and CeO 2 )
Attrition Highly resistant Not very resistant
resistance
Cost and life More expensive and longer Less expensive and lower life
life time time
HTFT, High-temperature Fischer Tropsch; LTFT, low-temperature Fischer Tropsch; WGS,
water gas shift.
7.3.1 Role of iron catalyst
High reactivity of iron carbides enhances the FT synthesis rate, and it is
easily accessible and relatively low-cost catalyst [32,61 63]. The main
role of iron catalysts is to stimulate the WGS reaction, which is favored
for lower ratio of H 2 /CO feed. The WGS reaction provides external
hydrogen for FT synthesis, which is necessary for syngas production from