Page 132 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 132
BATTERY DESIGN 5.9
To minimize the possibility of physically reversing a battery, the proper battery orientation should
be clearly marked on the device, with simple and clear instructions. Blind battery compartments,
where the individual batteries are not visible, should be avoided. The best practice is to use oriented
or polarized battery holders, as discussed previously.
A suggested approach is to design the cell cavities for single cells so there are no strings of cells
that could allow an incorrect reversal insertion of one cell. This does add cost to the device by requir-
ing additional contacts, but it ensures that the circuit is correctly completed (by virtue of the physical
connection of the cells by the device’s circuit). Such a design is strongly suggested when a device
can accept primary and rechargeable cells of a particular size, such as the AA or AAA sizes, which
are commonly available in primary alkaline, rechargeable nickel, or primary lithium.
5.3.2 Battery Dimensions
At times, equipment manufacturers may design the battery cavity of their device around the battery
of a single manufacturer. Unfortunately, the batteries made by the various manufacturers are not
exactly the same size. While the differences may not be great, this could result in a cavity design
that will not accept batteries of all manufacturers.
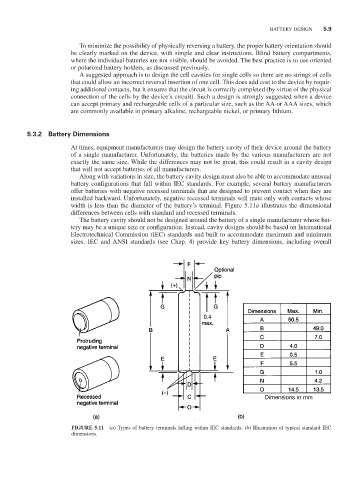
Along with variations in size, the battery cavity design must also be able to accommodate unusual
battery configurations that fall within IEC standards. For example, several battery manufacturers
offer batteries with negative recessed terminals that are designed to prevent contact when they are
installed backward. Unfortunately, negative recessed terminals will mate only with contacts whose
width is less than the diameter of the battery’s terminal. Figure 5.11a illustrates the dimensional
differences between cells with standard and recessed terminals.
The battery cavity should not be designed around the battery of a single manufacturer whose bat-
tery may be a unique size or configuration. Instead, cavity designs should be based on International
Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards and built to accommodate maximum and minimum
sizes. IEC and ANSI standards (see Chap. 4) provide key battery dimensions, including overall
FIGURE 5.11 (a) Types of battery terminals falling within IEC standards. (b) Illustration of typical standard IEC
dimensions.