Page 135 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 135
5.12 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
(c)
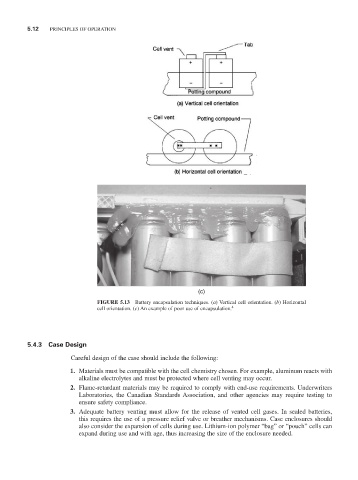
FIGURE 5.13 Battery encapsulation techniques. (a) Vertical cell orientation. (b) Horizontal
4
cell orientation. (c) An example of poor use of encapsulation.
5.4.3 Case Design
Careful design of the case should include the following:
1. Materials must be compatible with the cell chemistry chosen. For example, aluminum reacts with
alkaline electrolytes and must be protected where cell venting may occur.
2. Flame-retardant materials may be required to comply with end-use requirements. Underwriters
Laboratories, the Canadian Standards Association, and other agencies may require testing to
ensure safety compliance.
3. Adequate battery venting must allow for the release of vented cell gases. In sealed batteries,
this requires the use of a pressure relief valve or breather mechanisms. Case enclosures should
also consider the expansion of cells during use. Lithium-ion polymer “bag” or “pouch” cells can
expand during use and with age, thus increasing the size of the enclosure needed.