Page 218 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 218
9.12 PRIMARY BATTERIES
1.6
1.5
1.4
1.3
1.2
Voltage 1.1
1 IC13 type 1
IC13 type 2
0.9
IC13 type 3
0.8 IC7
0.7
0.6
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
mAh/g manganese oxide
(b)
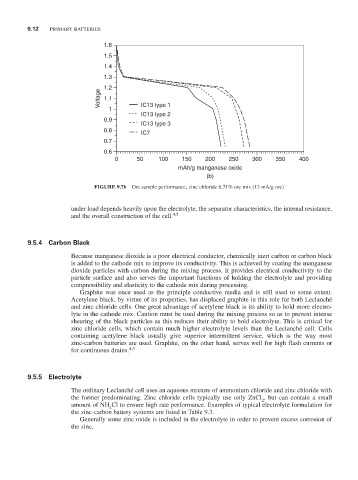
FIGURE 9.7b Ore sample performance, zinc chloride 6.71% ore mix (13 mA/g ore)
under load depends heavily upon the electrolyte, the separator characteristics, the internal resistance,
and the overall construction of the cell. 4,5
9.5.4 Carbon Black
Because manganese dioxide is a poor electrical conductor, chemically inert carbon or carbon black
is added to the cathode mix to improve its conductivity. This is achieved by coating the manganese
dioxide particles with carbon during the mixing process. It provides electrical conductivity to the
particle surface and also serves the important functions of holding the electrolyte and providing
compressibility and elasticity to the cathode mix during processing.
Graphite was once used as the principle conductive media and is still used to some extent.
Acetylene black, by virtue of its properties, has displaced graphite in this role for both Leclanché
and zinc chloride cells. One great advantage of acetylene black is its ability to hold more electro-
lyte in the cathode mix. Caution must be used during the mixing process so as to prevent intense
shearing of the black particles as this reduces their ability to hold electrolyte. This is critical for
zinc chloride cells, which contain much higher electrolyte levels than the Leclanché cell. Cells
containing acetylene black usually give superior intermittent service, which is the way most
zinc-carbon batteries are used. Graphite, on the other hand, serves well for high flash currents or
for continuous drains. 4,9
9.5.5 Electrolyte
The ordinary Leclanché cell uses an aqueous mixture of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride with
the former predominating. Zinc chloride cells typically use only ZnCl , but can contain a small
2
amount of NH Cl to ensure high rate performance. Examples of typical electrolyte formulation for
4
the zinc-carbon battery systems are listed in Table 9.3.
Generally some zinc oxide is included in the electrolyte in order to prevent excess corrosion of
the zinc.