Page 221 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 221
ZINC-CARBON BATTERIES—LECLANCHÉ AND ZINC CHLORIDE CELL SYSTEMS 9.15
9.5.10 Jacket
The battery jacket can be made of various components: metal, paper, plastic, polymer films, plain
or asphalt-lined cardboard, or foil in combination or alone. The jacket provides strength, protection,
leakage prevention, electrical isolation, decoration, and a site for the manufacturer’s label. In many
manufacturers’ designs, the jacket is an integral part of the sealing system. It locks some seals in
place, provides a vent path for the escape of gases, or acts as a supporting member to allow seals to
flex under internal gas pressures. In the inside-out construction, the jacket was the container in which
a carbon-wax collector was impact-molded (Fig. 9.5).
9.5.11 Electrical Contacts
The top and bottom of most batteries are capped with shiny, tin-plated steel (or brass) terminals to
aid conductivity, prevent exposure of any zinc, and in many designs enhance the appearance of the
cell. Some of the bottom covers are swaged onto the zinc can, others are locked into paper jackets or
captured under the jacket crimp. Top covers are almost always fitted onto the carbon electrode with
interference. All of the designs try to minimize the electrical contact resistance.
9.6 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
9.6.1 Voltage
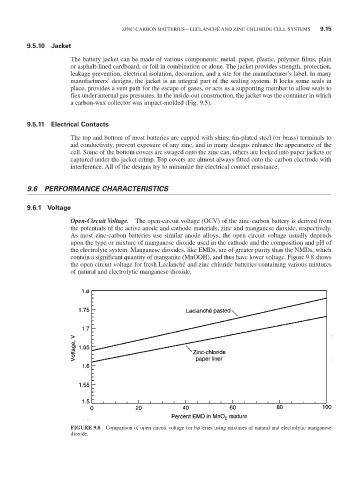
Open-Circuit Voltage. The open-circuit voltage (OCV) of the zinc-carbon battery is derived from
the potentials of the active anode and cathode materials, zinc and manganese dioxide, respectively.
As most zinc-carbon batteries use similar anode alloys, the open circuit voltage usually depends
upon the type or mixture of manganese dioxide used in the cathode and the composition and pH of
the electrolyte system. Manganese dioxides, like EMDs, are of greater purity than the NMDs, which
contain a significant quantity of manganite (MnOOH), and thus have lower voltage. Figure 9.8 shows
the open circuit voltage for fresh Leclanché and zinc chloride batteries containing various mixtures
of natural and electrolytic manganese dioxide.
FIGURE 9.8 Comparison of open-circuit voltage for batteries using mixtures of natural and electrolytic manganese
dioxide.