Page 226 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 226
9.20 PRIMARY BATTERIES
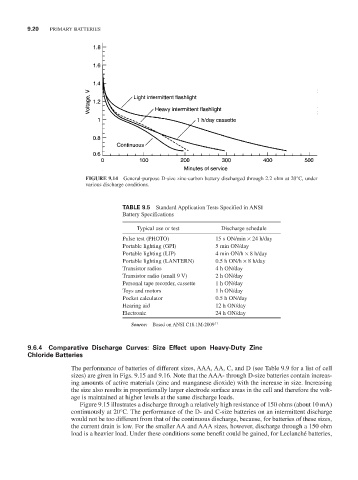
FIGURE 9.14 General-purpose D-size zinc-carbon battery discharged through 2.2 ohm at 20°C, under
various discharge conditions.
TABLE 9.5 Standard Application Tests Specified in ANSI
Battery Specifications
Typical use or test Discharge schedule
Pulse test (PHOTO) 15 s ON/min × 24 h/day
Portable lighting (GPI) 5 min ON/day
Portable lighting (LIP) 4 min ON/h × 8 h/day
Portable lighting (LANTERN) 0.5 h ON/h × 8 h/day
Transistor radios 4 h ON/day
Transistor radio (small 9 V) 2 h ON/day
Personal tape recorder, cassette 1 h ON/day
Toys and motors 1 h ON/day
Pocket calculator 0.5 h ON/day
Hearing aid 12 h ON/day
Electronic 24 h ON/day
Source: Based on ANSI C18.1M-2009 11
9.6.4 Comparative Discharge Curves: Size Effect upon Heavy-Duty Zinc
Chloride Batteries
The performance of batteries of different sizes, AAA, AA, C, and D (see Table 9.9 for a list of cell
sizes) are given in Figs. 9.15 and 9.16. Note that the AAA- through D-size batteries contain increas-
ing amounts of active materials (zinc and manganese dioxide) with the increase in size. Increasing
the size also results in proportionally larger electrode surface areas in the cell and therefore the volt-
age is maintained at higher levels at the same discharge loads.
Figure 9.15 illustrates a discharge through a relatively high resistance of 150 ohms (about 10 mA)
continuously at 20°C. The performance of the D- and C-size batteries on an intermittent discharge
would not be too different from that of the continuous discharge, because, for batteries of these sizes,
the current drain is low. For the smaller AA and AAA sizes, however, discharge through a 150 ohm
load is a heavier load. Under these conditions some benefit could be gained, for Leclanché batteries,