Page 306 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 306
13.12 PrImArY BATTErIES
1.6
20°C 1.6
20°C
1.4
0°C 1.4
Voltage, V 1.2 –20°C Voltage, V 1.2 0°C
1.0 –10°C
1.0
50 100 200 500 1k 2k 100 200 500 1k 2k 5k
Load, ohms Load, ohms
(a) Type 396 cell, 7.9 × 2.7 mm (b) Type 357 cell, 11.6 × 5.35 mm
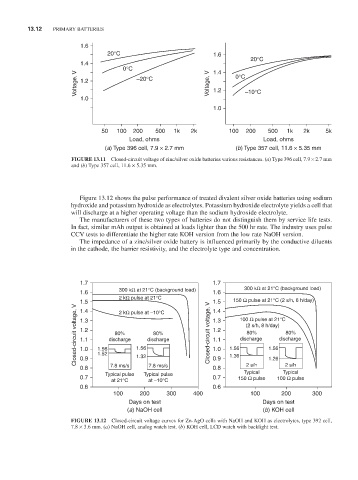
FiGURE 13.11 Closed-circuit voltage of zinc/silver oxide batteries various resistances. (a) Type 396 cell, 7.9 × 2.7 mm
and (b) Type 357 cell, 11.6 × 5.35 mm.
Figure 13.12 shows the pulse performance of treated divalent silver oxide batteries using sodium
hydroxide and potassium hydroxide as electrolytes. Potassium hydroxide electrolyte yields a cell that
will discharge at a higher operating voltage than the sodium hydroxide electrolyte.
The manufacturers of these two types of batteries do not distinguish them by service life tests.
In fact, similar mAh output is obtained at loads lighter than the 500 hr rate. The industry uses pulse
CCV tests to differentiate the higher rate KOH version from the low rate naOH version.
The impedance of a zinc/silver oxide battery is influenced primarily by the conductive diluents
in the cathode, the barrier resistivity, and the electrolyte type and concentration.
1.7 1.7
1.6 300 kΩ at 21°C (background load) 1.6 300 kΩ at 21°C (background load)
2 kΩ pulse at 21°C
1.5 2 kΩ pulse at –10°C 1.5 150 Ω pulse at 21°C (2 s/h, 6 h/day)
Closed-circuit voltage, V 1.3 1.56 discharge 1.56 discharge Closed-circuit voltage, V 1.3 1.56 100 Ω pulse at 21°C 80%
1.4
1.4
(2 s/h, 8 h/day)
1.2
1.2
80%
80%
80%
discharge
discharge
1.1
1.1
1.0
1.0
1.56
0.9
2 s/h
2 s/h
0.8
0.8 1.52 7.8 ms/s 1.32 7.8 ms/s 0.9 1.36 Typical 1.26 Typical
0.7 Typical pulse Typical pulse 0.7 150 Ω pulse 100 Ω pulse
at 21°C at –10°C
0.6 0.6
100 200 300 400 100 200 300
Days on test Days on test
(a) NaOH cell (b) KOH cell
FiGURE 13.12 Closed-circuit voltage curves for Zn-AgO cells with naOH and KOH as electrolytes, type 392 cell,
7.8 × 3.6 mm. (a) naOH cell, analog watch test. (b) KOH cell, LCD watch with backlight test.