Page 335 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 335
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.3
TABLE 14.1 Classification of Lithium Primary Batteries*
Operating Shelf Nominal
Cell Typical Power Size, range, life, Typical cell voltage, Key
classification electrolyte capability Ah °C years cathodes V characteristics
Soluble cathode Organic or Moderate 0.5 to 10,000 -80 to 70 5–20 SO 2 3.0 High energy output,
(liquid or gas) inorganic to high SOCl 2 3.6 high power output,
(w/solute) power, W SO Cl 3.9 low-temperature
2 2
operation, long
shelf life
Solid cathode Organic Low to 0.03 to 1200 -40 to 50 5–8 V O 5 3.3 High energy output
2
(w/solute) moderate AgV O 5.5 3.2 for moderate power
2
power, MnO 2 3.0 requirements, non-
mW-W CFx 2.6 pressurized cells
CuS 1.7
FeS 2 1.5
FeS 1.5
Solid electrolyte Solid state Very low 0.003 to 2.4 0 to 100 10–25 Pbi /PbS/Pb 1.9 excellent shelf life,
2
(see Chap. 31) power, μW i (P2VP) 2.8 solid state—no
2
leakage, long-term
microampere
discharge
*For reserve lithium batteries, see Chap. 35.
available in low-rate and the moderate-rate jelly-roll configurations. A number of different solid cath-
odes are being used in lithium primary cells, as listed in Table 14.1. The discharge of the solid-cathode
cells is not as flat as that of the soluble-cathode cells, but at the lower discharge rates and ambient tem-
perature, their capacity (energy density) may be higher than that of the lithium/sulfur dioxide cell.
Solid-Electrolyte Cells. These cells are noted for their extremely long storage life, in excess of
20 years, but are capable of only low-rate discharge in the microampere range. They are used in
applications such as memory backup, cardiac pacemakers, and similar equipment where current
requirements are low, but long life is critical (see Chap. 31).
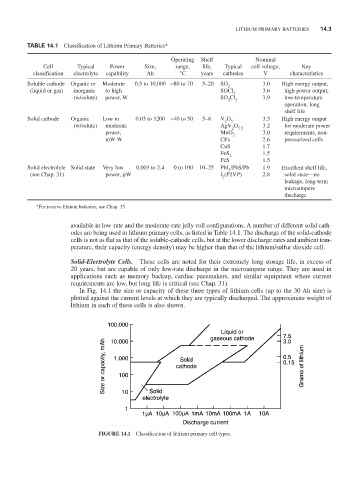
in Fig. 14.1 the size or capacity of these three types of lithium cells (up to the 30 Ah size) is
plotted against the current levels at which they are typically discharged. The approximate weight of
lithium in each of these cells is also shown.
FIGURE 14.1 Classification of lithium primary cell types.