Page 416 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 416
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.81
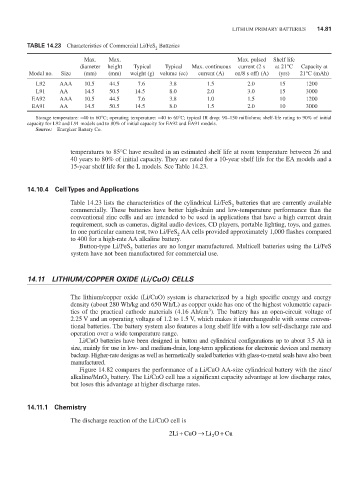
TABLE 14.23 Characteristics of Commercial Li/FeS Batteries
2
Max. Max. Max. pulsed Shelf life
diameter height Typical Typical Max. continuous current (2 s at 21°C Capacity at
Model no. Size (mm) (mm) weight (g) volume (cc) current (A) on/8 s off) (A) (yrs) 21°C (mAh)
L92 AAA 10.5 44.5 7.6 3.8 1.5 2.0 15 1200
L91 AA 14.5 50.5 14.5 8.0 2.0 3.0 15 3000
eA92 AAA 10.5 44.5 7.6 3.8 1.0 1.5 10 1200
eA91 AA 14.5 50.5 14.5 8.0 1.5 2.0 10 3000
Storage temperature: -40 to 60°C; operating temperature: -40 to 60°C; typical ir drop: 90–150 milliohms; shelf-life rating to 90% of initial
capacity for L92 and L91 models and to 80% of initial capacity for eA92 and eA91 models.
Source: energizer Battery Co.
temperatures to 85°C have resulted in an estimated shelf life at room temperature between 26 and
40 years to 80% of initial capacity. They are rated for a 10-year shelf life for the eA models and a
15-year shelf life for the L models. See Table 14.23.
14.10.4 Cell Types and Applications
Table 14.23 lists the characteristics of the cylindrical Li/FeS batteries that are currently available
2
commercially. These batteries have better high-drain and low-temperature performance than the
conventional zinc cells and are intended to be used in applications that have a high current drain
requirement, such as cameras, digital audio devices, CD players, portable lighting, toys, and games.
in one particular camera test, two Li/FeS AA cells provided approximately 1,000 flashes compared
2
to 400 for a high-rate AA alkaline battery.
Button-type Li/FeS batteries are no longer manufactured. Multicell batteries using the Li/FeS
2
system have not been manufactured for commercial use.
14.11 LITHIUM/COPPER OXIDE (Li/CuO) CELLS
The lithium/copper oxide (Li/CuO) system is characterized by a high specific energy and energy
density (about 280 Wh/kg and 650 Wh/L) as copper oxide has one of the highest volumetric capaci-
3
ties of the practical cathode materials (4.16 Ah/cm ). The battery has an open-circuit voltage of
2.25 V and an operating voltage of 1.2 to 1.5 V, which makes it interchangeable with some conven-
tional batteries. The battery system also features a long shelf life with a low self-discharge rate and
operation over a wide temperature range.
Li/CuO batteries have been designed in button and cylindrical configurations up to about 3.5 Ah in
size, mainly for use in low- and medium-drain, long-term applications for electronic devices and memory
backup. Higher-rate designs as well as hermetically sealed batteries with glass-to-metal seals have also been
manufactured.
Figure 14.82 compares the performance of a Li/CuO AA-size cylindrical battery with the zinc/
alkaline/MnO battery. The Li/CuO cell has a significant capacity advantage at low discharge rates,
2
but loses this advantage at higher discharge rates.
14.11.1 Chemistry
The discharge reaction of the Li/CuO cell is
+
2Li CuO → LiO Cu
+
2