Page 412 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 412
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.77
14.10.2 Construction
Li/FeS batteries may be manufactured in a variety of designs, including the button and both bobbin
2
and spiral-wound-electrode cylindrical cells. A bobbin construction is most suitable for light-drain
applications. The spiral-wound-electrode construction is needed for the heavier-drain applications,
and it is this design that has been commercialized.
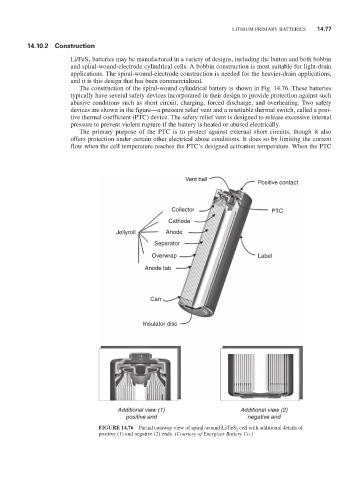
The construction of the spiral-wound cylindrical battery is shown in Fig. 14.76. These batteries
typically have several safety devices incorporated in their design to provide protection against such
abusive conditions such as short circuit, charging, forced discharge, and overheating. Two safety
devices are shown in the figure—a pressure relief vent and a resettable thermal switch, called a posi-
tive thermal coefficient (PTC) device. The safety relief vent is designed to release excessive internal
pressure to prevent violent rupture if the battery is heated or abused electrically.
The primary purpose of the PTC is to protect against external short circuits, though it also
offers protection under certain other electrical abuse conditions. it does so by limiting the current
flow when the cell temperature reaches the PTC’s designed activation temperature. When the PTC
Vent ball
Positive contact
Collector PTC
Cathode
Jellyroll Anode
Separator
Overwrap Label
Anode tab
Can
Insulator disc
Additional view (1) Additional view (2)
positive end negative end
FIGURE 14.76 Partial cutaway view of spiral-wound Li/FeS cell with additional details of
2
positive (1) and negative (2) ends. (Courtesy of Energizer Battery Co.)