Page 56 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 56
ELECTROCHEMICAL PRINCIPLES AND REACTIONS 2.13
– –
– – Cs + Electrolyte
Electrode Electrolyte Electrode
–
–
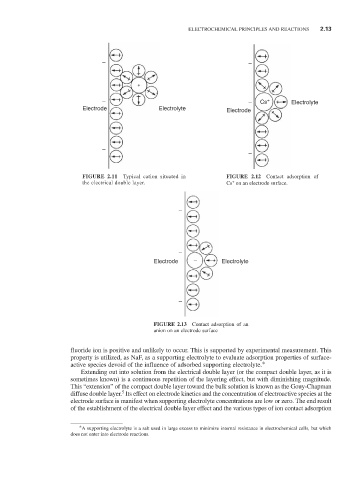
FIGURE 2.11 Typical cation situated in FIGURE 2.12 Contact adsorption of
+
the electrical double layer. Cs on an electrode surface.
–
–
Electrode – Electrolyte
–
FIGURE 2.13 Contact adsorption of an
anion on an electrode surface
fluoride ion is positive and unlikely to occur. This is supported by experimental measurement. This
property is utilized, as NaF, as a supporting electrolyte to evaluate adsorption properties of surface-
active species devoid of the influence of adsorbed supporting electrolyte.*
Extending out into solution from the electrical double layer (or the compact double layer, as it is
sometimes known) is a continuous repetition of the layering effect, but with diminishing magnitude.
This “extension” of the compact double layer toward the bulk solution is known as the Gouy-Chapman
diffuse double layer. Its effect on electrode kinetics and the concentration of electroactive species at the
5
electrode surface is manifest when supporting electrolyte concentrations are low or zero. The end result
of the establishment of the electrical double layer effect and the various types of ion contact adsorption
*A supporting electrolyte is a salt used in large excess to minimize internal resistance in electrochemical cells, but which
does not enter into electrode reactions.