Page 129 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 129
5.6 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
current from flowing through the cell. This limits the extent of the voltage reversal to that of the
characteristic of the diode.
5.2.4 Protection of Primary Cells and Batteries from External Charge
Many battery-powered devices are also operated from rectified alternating-current (AC) sources. These
could include devices that offer both AC and battery operation or devices that use the battery for backup
when the AC power supply fails or is not available. Both primary lithium as well as other chemistries such
as alkaline are commonly used in devices that operate from both battery power and AC power sources.
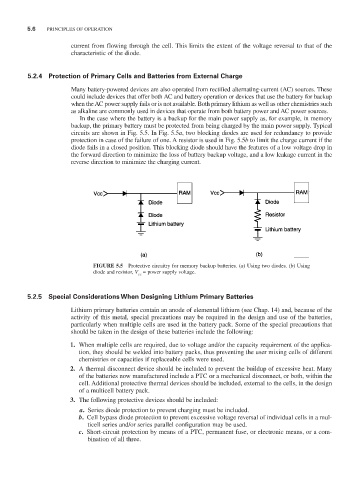
In the case where the battery is a backup for the main power supply as, for example, in memory
backup, the primary battery must be protected from being charged by the main power supply. Typical
circuits are shown in Fig. 5.5. In Fig. 5.5a, two blocking diodes are used for redundancy to provide
protection in case of the failure of one. A resistor is used in Fig. 5.5b to limit the charge current if the
diode fails in a closed position. This blocking diode should have the features of a low voltage drop in
the forward direction to minimize the loss of battery backup voltage, and a low leakage current in the
reverse direction to minimize the charging current.
FIGURE 5.5 Protective circuitry for memory backup batteries. (a) Using two diodes. (b) Using
diode and resistor, V = power supply voltage.
cc
5.2.5 Special Considerations When Designing Lithium Primary Batteries
Lithium primary batteries contain an anode of elemental lithium (see Chap. 14) and, because of the
activity of this metal, special precautions may be required in the design and use of the batteries,
particularly when multiple cells are used in the battery pack. Some of the special precautions that
should be taken in the design of these batteries include the following:
1. When multiple cells are required, due to voltage and/or the capacity requirement of the applica-
tion, they should be welded into battery packs, thus preventing the user mixing cells of different
chemistries or capacities if replaceable cells were used.
2. A thermal disconnect device should be included to prevent the buildup of excessive heat. Many
of the batteries now manufactured include a PTC or a mechanical disconnect, or both, within the
cell. Additional protective thermal devices should be included, external to the cells, in the design
of a multicell battery pack.
3. The following protective devices should be included:
a. Series diode protection to prevent charging must be included.
b. Cell bypass diode protection to prevent excessive voltage reversal of individual cells in a mul-
ticell series and/or series parallel configuration may be used.
c. Short-circuit protection by means of a PTC, permanent fuse, or electronic means, or a com-
bination of all three.