Page 180 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 180
[55] 462 1:2MPa 105 C 0:925 1890kJ=kg kJ/kg Continued
B 0 1660 377
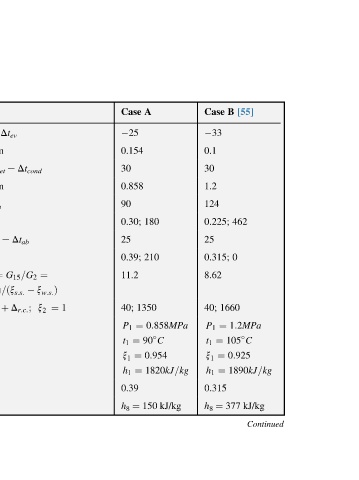
Case 33 0.1 30 1.2 124 0.225; 25 0.315; 8.62 40; ¼ P 1 ¼ t 1 ¼ x 1 ¼ h 1 0.315 ¼ h 8
0:858MPa 1820kJ=kg kJ/kg
180 210 90 C 0:954
A 1350 150
Case 25 0.154 30 0.858 90 0.30; 25 0.39; 11.2 40; ¼ P 1 ¼ t 1 ¼ x 1 ¼ h 1 0.39 ¼ h 8
1 ¼
¼ x w:s: Þ x 2
Dt cond Dt ab G 15 =G 2
Dt ev e e þ D r:c: ;
TS-diagram t c.w.outlet TS-diagram Dt gen t input.app. ¼ x w:s: Þ=ðx s:s: t c:w:outlet
Formula t b.outlet ¼ t 0 by ¼ t cond by e t s ¼ t 9 h 9 x w.s. ; ¼ t 13 h 13 x s.s. ; G s:s: =D ¼ f ¼ðx 2 ¼ t 2 e x 13 ¼ x 8 e
C C kJ/kg
output, outlet, C; outlet:
C generator 8
temperature, MPa pressure, C generator at kJ/kg absorber at kJ/kg condenser, reflux at point at
Solution. evaporation evaporation temperature, MPa pressure, temperature parameters, temperature parameters, ratios circulation after parameters parameters vapor concentration solution the of
4.E2 Parameters agent Condensation Condenser solution solution solution solution Equilibrium enthalpy
Table Cooling Ammonia Weak Weak Strong Strong Solution Steam Mixture The