Page 45 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 45
Principles and operation of refrigeration and heat pump systems 33
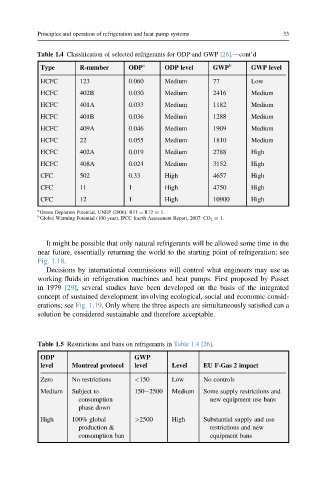
Table 1.4 Classification of selected refrigerants for ODP and GWP [26].dcont’d
Type R-number ODP a ODP level GWP b GWP level
HCFC 123 0.060 Medium 77 Low
HCFC 402B 0.030 Medium 2416 Medium
HCFC 401A 0.033 Medium 1182 Medium
HCFC 401B 0.036 Medium 1288 Medium
HCFC 409A 0.046 Medium 1909 Medium
HCFC 22 0.055 Medium 1810 Medium
HCFC 402A 0.019 Medium 2788 High
HCFC 408A 0.024 Medium 3152 High
CFC 502 0.33 High 4657 High
CFC 11 1 High 4750 High
CFC 12 1 High 10900 High
a
Ozone Depletion Potential, UNEP (2006): R11 ¼ R12 h 1.
b
Global Warming Potential (100 year), IPCC fourth Assessment Report, 2007: CO 2 h 1.
It might be possible that only natural refrigerants will be allowed some time in the
near future, essentially returning the world to the starting point of refrigeration; see
Fig. 1.18.
Decisions by international commissions will control what engineers may use as
working fluids in refrigeration machines and heat pumps. First proposed by Passet
in 1979 [29], several studies have been developed on the basis of the integrated
concept of sustained development involving ecological, social and economic consid-
erations; see Fig. 1.19. Only where the three aspects are simultaneously satisfied can a
solution be considered sustainable and therefore acceptable.
Table 1.5 Restrictions and bans on refrigerants in Table 1.4 [26].
ODP GWP
level Montreal protocol level Level EU F-Gas 2 impact
Zero No restrictions <150 Low No controls
Medium Subject to 150e2500 Medium Some supply restrictions and
consumption new equipment use bans
phase down
High 100% global >2500 High Substantial supply and use
production & restrictions and new
consumption ban equipment bans