Page 88 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 88
Characteristics of low-temperature energy sources for heat pumps 77
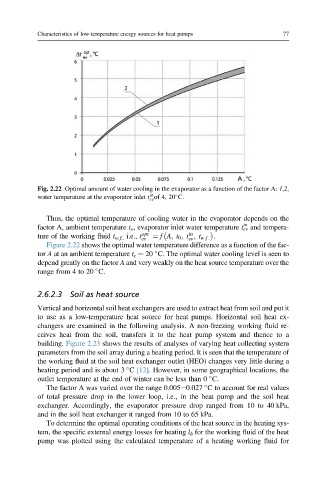
Fig. 2.22 Optimal amount of water cooling in the evaporator as a function of the factor A: 1,2,
in
water temperature at the evaporator inlet t of 4, 20 C.
ev
Thus, the optimal temperature of cooling water in the evaporator depends on the
in
factor A, ambient temperature t o , evaporator inlet water temperature t ev and tempera-
in
ture of the working fluid t w.f., i.e., t opt ¼ f A; t 0 ; t ; t w:f : .
ev ev
Figure 2.22 shows the optimal water temperature difference as a function of the fac-
tor A at an ambient temperature t e ¼ 20 C. The optimal water cooling level is seen to
depend greatly on the factor A and very weakly on the heat source temperature over the
range from 4 to 20 C.
2.6.2.3 Soil as heat source
Vertical and horizontal soil heat exchangers are used to extract heat from soil and put it
to use as a low-temperature heat source for heat pumps. Horizontal soil heat ex-
changers are examined in the following analysis. A non-freezing working fluid re-
ceives heat from the soil, transfers it to the heat pump system and thence to a
building. Figure 2.23 shows the results of analyses of varying heat collecting system
parameters from the soil array during a heating period. It is seen that the temperature of
the working fluid at the soil heat exchanger outlet (HEO) changes very little during a
heating period and is about 3 C [12]. However, in some geographical locations, the
outlet temperature at the end of winter can be less than 0 C.
The factor A was varied over the range 0.005e0.027 C to account for real values
of total pressure drop in the lower loop, i.e., in the heat pump and the soil heat
exchanger. Accordingly, the evaporator pressure drop ranged from 10 to 40 kPa,
and in the soil heat exchanger it ranged from 10 to 65 kPa.
To determine the optimal operating conditions of the heat source in the heating sys-
tem, the specific external energy losses for heating l h for the working fluid of the heat
pump was plotted using the calculated temperature of a heating working fluid for