Page 113 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 113
98 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
R
and V = R + 2 R V
2
2
1
R 1 i 1
i R 1 i R 2 i i i
R 2
V 1 V 2 i 2
V
V
(a) Resistors in series (b) Resistors in parallel
Fig. 2.2
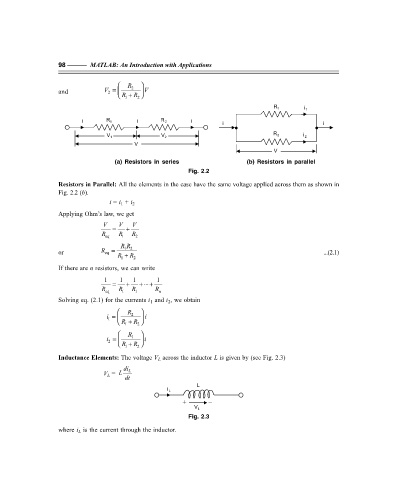
Resistors in Parallel: All the elements in the case have the same voltage applied across them as shown in
Fig. 2.2 (b).
i = i 1 + i 2
Applying Ohm’s law, we get
V = V + V
R eq R 1 R 2
RR
12
or R = R + R 2 ...(2.1)
eq
1
If there are n resistors, we can write
1 = 1 + 1 + ... + 1
R eq R 1 R 1 R n
Solving eq. (2.1) for the currents i 1 and i 2 , we obtain
R
i = 2 i
1 R + R
1
2
R
i = 1 i
2 R + R
2
1
Inductance Elements: The voltage V L across the inductor L is given by (see Fig. 2.3)
di
V L = L L
dt
L
i L
+ –
V L
Fig. 2.3
where i L is the current through the inductor.
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09