Page 251 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 251
236 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
24
x10
4
3
error
Normalized 2
1
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Iteration #
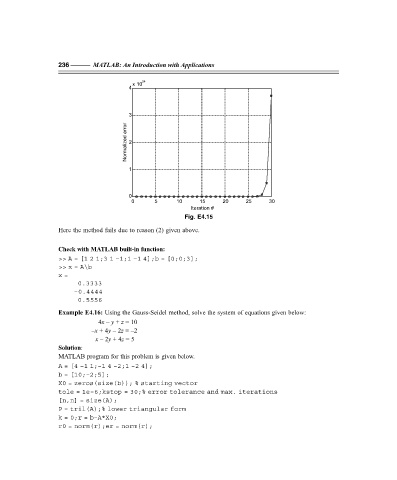
Fig. E4.15
Here the method fails due to reason (2) given above.
Check with MATLAB built-in function:
>> A = [1 2 1;3 1 –1;1 –1 4];b = [0;0;3];
>> x = A\b
x =
0.3333
–0.4444
0.5556
Example E4.16: Using the Gauss-Seidel method, solve the system of equations given below:
4x – y + z = 10
–x + 4y – 2z = –2
x – 2y + 4z = 5
Solution:
MATLAB program for this problem is given below.
A = [4 –1 1;–1 4 –2;1 –2 4];
b = [10;–2;5];
X0 = zeros(size(b)); % starting vector
tole = 1e–6;kstop = 30;% error tolerance and max. iterations
[n,n] = size(A);
P = tril(A);% lower triangular form
k = 0;r = b–A*X0;
r0 = norm(r);er = norm(r);