Page 231 - MATLAB Recipes for Earth Sciences
P. 231
9.4 Independent Component Analysis (by N. Marwan) 227
Raw Signals Mixed Signals
0.5 0.5
0
s 1 0 x 1
−0.5
−0.5 −1
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000
a b
0.5 0.4
0.2
0
s 2 x 2 0
−0.5
−0.2
−1 −0.4
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000
c d
1 2
0.5 1
s 3 0 x 3 0
−0.5 −1
−1 −2
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 0 1000 2000 3000 4000
e f
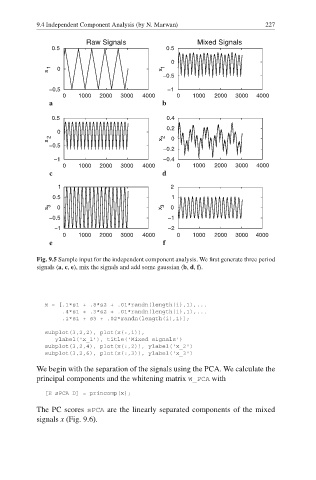
Fig. 9.5 Sample input for the independent component analysis. We first generate three period
signals (a, c, e), mix the signals and add some gaussian (b, d, f).
x = [.1*s1 + .8*s2 + .01*randn(length(i),1),...
.4*s1 + .3*s2 + .01*randn(length(i),1),...
.1*s1 + s3 + .02*randn(length(i),1)];
subplot(3,2,2), plot(x(:,1)),
ylabel('x_1'), title('Mixed signals')
subplot(3,2,4), plot(x(:,2)), ylabel('x_2')
subplot(3,2,6), plot(x(:,3)), ylabel('x_3')
We begin with the separation of the signals using the PCA. We calculate the
principal components and the whitening matrix W_PCA with
[E sPCA D] = princomp(x);
The PC scores sPCA are the linearly separated components of the mixed
signals x (Fig. 9.6).