Page 122 - MEMS Mechanical Sensors
P. 122
5.7 Smart Sensors 111
Sensing Analog
element Amp process
Measurand
Monitoring
Excitation Self-test
control
Control Memory Data
processor conversion
Data Digital
comms process
Sensor bus
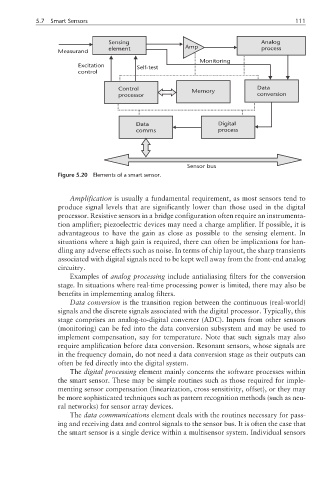
Figure 5.20 Elements of a smart sensor.
Amplification is usually a fundamental requirement, as most sensors tend to
produce signal levels that are significantly lower than those used in the digital
processor. Resistive sensors in a bridge configuration often require an instrumenta-
tion amplifier; piezoelectric devices may need a charge amplifier. If possible, it is
advantageous to have the gain as close as possible to the sensing element. In
situations where a high gain is required, there can often be implications for han-
dling any adverse effects such as noise. In terms of chip layout, the sharp transients
associated with digital signals need to be kept well away from the front-end analog
circuitry.
Examples of analog processing include antialiasing filters for the conversion
stage. In situations where real-time processing power is limited, there may also be
benefits in implementing analog filters.
Data conversion is the transition region between the continuous (real-world)
signals and the discrete signals associated with the digital processor. Typically, this
stage comprises an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Inputs from other sensors
(monitoring) can be fed into the data conversion subsystem and may be used to
implement compensation, say for temperature. Note that such signals may also
require amplification before data conversion. Resonant sensors, whose signals are
in the frequency domain, do not need a data conversion stage as their outputs can
often be fed directly into the digital system.
The digital processing element mainly concerns the software processes within
the smart sensor. These may be simple routines such as those required for imple-
menting sensor compensation (linearization, cross-sensitivity, offset), or they may
be more sophisticated techniques such as pattern recognition methods (such as neu-
ral networks) for sensor array devices.
The data communications element deals with the routines necessary for pass-
ing and receiving data and control signals to the sensor bus. It is often the case that
the smart sensor is a single device within a multisensor system. Individual sensors