Page 117 - MEMS Mechanical Sensors
P. 117
106 Mechanical Transduction Techniques
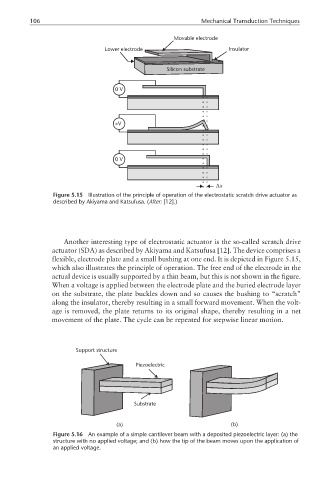
Movable electrode
Lower electrode Insulator
Silicon substrate
0V
+V
0V
∆x
Figure 5.15 Illustration of the principle of operation of the electrostatic scratch drive actuator as
described by Akiyama and Katsufusa. (After: [12].)
Another interesting type of electrostatic actuator is the so-called scratch drive
actuator (SDA) as described by Akiyama and Katsufusa [12]. The device comprises a
flexible, electrode plate and a small bushing at one end. It is depicted in Figure 5.15,
which also illustrates the principle of operation. The free end of the electrode in the
actual device is usually supported by a thin beam, but this is not shown in the figure.
When a voltage is applied between the electrode plate and the buried electrode layer
on the substrate, the plate buckles down and so causes the bushing to “scratch”
along the insulator, thereby resulting in a small forward movement. When the volt-
age is removed, the plate returns to its original shape, thereby resulting in a net
movement of the plate. The cycle can be repeated for stepwise linear motion.
Support structure
Piezoelectric
Substrate
(a) (b)
Figure 5.16 An example of a simple cantilever beam with a deposited piezoelectric layer: (a) the
structure with no applied voltage; and (b) how the tip of the beam moves upon the application of
an applied voltage.