Page 249 - MEMS and Microstructures in Aerospace Applications
P. 249
Osiander / MEMS and microstructures in Aerospace applications DK3181_c011 Final Proof page 240 1.9.2005 12:31pm
240 MEMS and Microstructures in Aerospace Applications
TABLE 11.2
Performance Characteristics for Vacuum Arc Thruster System
I sp 1000 to 3000 sec
I-bit 10 nN to 30 mN sec
Rep. rate Single shot 1 kHz
Power 10 W (30 W)
Thrust/Power 10 nN to 300 mN/W
Impulse/prop. 10 mN/w
10 N sec/g
Feed mechan. Yes
Impulse/sys.-mass 100 N sec/500 g
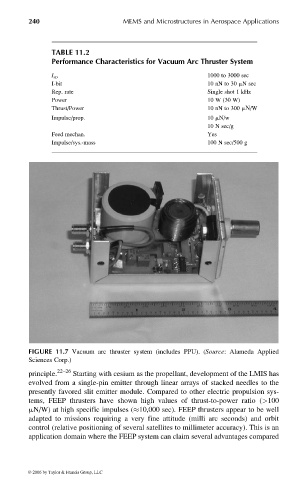
FIGURE 11.7 Vacuum arc thruster system (includes PPU). (Source: Alameda Applied
Sciences Corp.)
principle. 22–26 Starting with cesium as the propellant, development of the LMIS has
evolved from a single-pin emitter through linear arrays of stacked needles to the
presently favored slit emitter module. Compared to other electric propulsion sys-
tems, FEEP thrusters have shown high values of thrust-to-power ratio (>100
mN/W) at high specific impulses ( 10,000 sec). FEEP thrusters appear to be well
adapted to missions requiring a very fine attitude (milli arc seconds) and orbit
control (relative positioning of several satellites to millimeter accuracy). This is an
application domain where the FEEP system can claim several advantages compared
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC