Page 30 - MEMS and Microstructures in Aerospace Applications
P. 30
Osiander / MEMS and microstructures in Aerospace applications DK3181_c002 Final Proof page 21 1.9.2005 11:49am
Vision for Microtechnology Space Missions 21
2.2.4 NMP ST6 INERTIAL STELLAR CAMERA
NASA’s NMP is sponsoring the development of the inertial stellar compass (ISC)
space avionics technology that combines MEMS inertial sensors (gyroscopes)
with a wide field-of-view active pixel sensor (APS) star camera in a compact,
6
multifunctional package. This technology development and maturation activity is
being performed by the Charles Stark Draper Laboratory (CSDL) for a Space
Technology-6 (ST6) flight validation experiment now scheduled to fly in 2005.
The ISC technology is one of several MEMS technology development activities
7
being pursued at CSDL and, in particular, is an outgrowth of earlier CSDL research
focused in the areas of MEMS-based guidance, navigation, and control (GN&C)
8
sensors or actuators and low-power MEMS-based space avionic systems for
space. 9
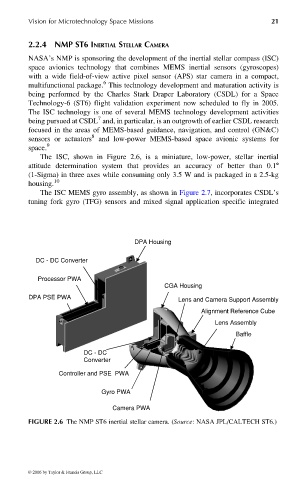
The ISC, shown in Figure 2.6, is a miniature, low-power, stellar inertial
attitude determination system that provides an accuracy of better than 0.18
(1-Sigma) in three axes while consuming only 3.5 W and is packaged in a 2.5-kg
housing. 10
The ISC MEMS gyro assembly, as shown in Figure 2.7, incorporates CSDL’s
tuning fork gyro (TFG) sensors and mixed signal application specific integrated
DPA Housing
DC - DC Converter
Processor PWA
CGA Housing
DPA PSE PWA Lens and Camera Support Assembly
Alignment Reference Cube
Lens Assembly
Baffle
DC - DC
Converter
Controller and PSE PWA
Gyro PWA
Camera PWA
FIGURE 2.6 The NMP ST6 inertial stellar camera. (Source: NASA JPL/CALTECH ST6.)
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC