Page 140 - Managing Global Warming
P. 140
Electricity generation in the world of nuclear power industry 105
In Europe, national variants of these LWR designs were then developed and deployed
l
in Sweden, Germany, France, while Korea and Japan followed a similar independent
development path.
After being cut out of nuclear cooperation agreements, and without pressure-vessel and fuel-
l
enrichment manufacturing capability, Canada and India developed their own Pressurized
Heavy Water Reactor (PHWR) designs, which were also internationally deployed in Paki-
stan (1 unit in 1972), Argentina (1 unit in 1984), South Korea (4units in 1983; 1997; 1998;
and 1999), Romania (2units in 1996 and 2007), and China (2units in 2002 and 2003).
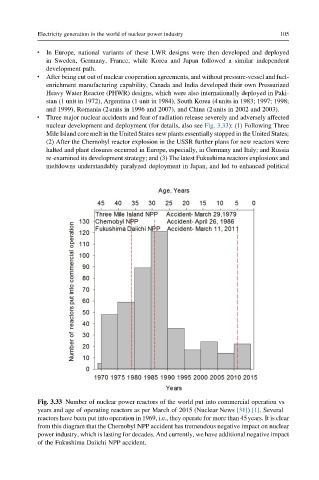
l Three major nuclear accidents and fear of radiation release severely and adversely affected
nuclear development and deployment (for details, also see Fig. 3.33): (1) Following Three
Mile Island core melt in the United States new plants essentially stopped in the United States;
(2) After the Chernobyl reactor explosion in the USSR further plans for new reactors were
halted and plant closures occurred in Europe, especially, in Germany and Italy; and Russia
re-examined its development strategy; and (3) The latest Fukushima reactors explosions and
meltdowns understandably paralyzed deployment in Japan, and led to enhanced political
Fig. 3.33 Number of nuclear power reactors of the world put into commercial operation vs
years and age of operating reactors as per March of 2015 (Nuclear News [31]) [1]. Several
reactors have been put into operation in 1969, i.e., they operate for more than 45years. It is clear
from this diagram that the Chernobyl NPP accident has tremendous negative impact on nuclear
power industry, which is lasting for decades. And currently, we have additional negative impact
of the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident.