Page 178 - Managing Global Warming
P. 178
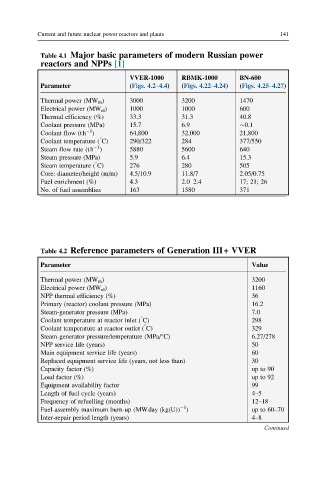
Current and future nuclear power reactors and plants 141
Table 4.1 Major basic parameters of modern Russian power
reactors and NPPs [1]
VVER-1000 RBMK-1000 BN-600
Parameter (Figs. 4.2–4.4) (Figs. 4.22–4.24) (Figs. 4.25–4.27)
Thermal power (MW th ) 3000 3200 1470
Electrical power (MW el ) 1000 1000 600
Thermal efficiency (%) 33.3 31.3 40.8
Coolant pressure (MPa) 15.7 6.9 0.1
1
Coolant flow (th ) 64,800 32,000 21,800
°
Coolant temperature ( C) 290/322 284 377/550
1
Steam flow rate (th ) 5880 5600 640
Steam pressure (MPa) 5.9 6.4 15.3
°
Steam temperature ( C) 276 280 505
Core: diameter/height (m/m) 4.5/10.9 11.8/7 2.05/0.75
Fuel enrichment (%) 4.3 2.0–2.4 17; 21; 26
No. of fuel assemblies 163 1580 371
Table 4.2 Reference parameters of Generation III+ VVER
Parameter Value
Thermal power (MW th ) 3200
Electrical power (MW el ) 1160
NPP thermal efficiency (%) 36
Primary (reactor) coolant pressure (MPa) 16.2
Steam-generator pressure (MPa) 7.0
°
Coolant temperature at reactor inlet ( C) 298
°
Coolant temperature at reactor outlet ( C) 329
Steam-generator pressure/temperature (MPa/°C) 6.27/278
NPP service life (years) 50
Main equipment service life (years) 60
Replaced equipment service life (years, not less than) 30
Capacity factor (%) up to 90
Load factor (%) up to 92
Equipment availability factor 99
Length of fuel cycle (years) 4–5
Frequency of refuelling (months) 12–18
1
Fuel-assembly maximum burn-up (MWday (kg(U)) ) up to 60–70
Inter-repair period length (years) 4–8
Continued