Page 205 - Managing Global Warming
P. 205
Current and future nuclear power reactors and plants 167
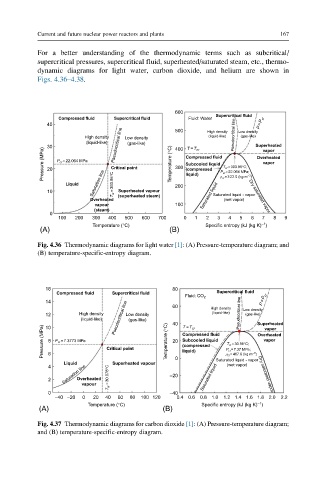
For a better understanding of the thermodynamic terms such as subcritical/
supercritical pressures, supercritical fluid, superheated/saturated steam, etc., thermo-
dynamic diagrams for light water, carbon dioxide, and helium are shown in
Figs. 4.36–4.38.
600
Compressed fluid Supercritical fluid Fluid: Water Supercritical fluid
40 500 P=P cr
(liquid-like)
(gas-like)
High density Low density High density Pseudocritical line Low density
(liquid-like) (gas-like)
30 Pseudocritical line 400 T=T cr Superheated
Pressure (MPa) 20 P cr = 22.064 MPa Critical point Temperature (°C) 300 Compressed fluid P cr = 22.064 MPa; Overheated
vapor
vapor
Subcooled liquid
T cr = 393.95°C;
(compressed
Liquid Saturation line T cr =393.95°C 200 liquid) r cr = 3 22.0 (kg m −3 )
10 Superheated vapour Saturated liquid - vapor
Overheated (superheated steam) Saturated liquid (wet vapor) Dry saturated vapor
vapour 100
(steam)
0
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
–1
Temperature (°C) Specific entropy (kJ (kg K) )
(A) (B)
Fig. 4.36 Thermodynamic diagrams for light water [1]: (A) Pressure-temperature diagram; and
(B) temperature-specific-entropy diagram.
16 80
Compressed fluid Supercritical fluid Supercritical fluid
Fluid: CO 2
14 60 P=P cr
(liquid-like)
(gas-like)
12 High density Low density High density Pseudocritical line Low density
(liquid-like) Pseudocritical line (gas-like) 40 T=T cr Superheated
Pressure (MPa) 8 P cr = 7.3773 MPa Critical point Temperature (°C) 20 Compressed fluid P cr = 7.37 MPa; Overheated
10
vapor
vapor
Subcooled liquid
T cr = 30.98°C;
(compressed
liquid)
6
Liquid Superheated vapour 0 Saturated liquid - vapor
Saturation line –20 r cr = 467.6 (kg m –3 ) Dry saturated vapor
4 (wet vapor)
2 Overheated T cr = 30.978°C Saturated liquid
vapour
0 –40
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2
–1
Temperature (°C) Specific entropy (kJ (kg K) )
(A) (B)
Fig. 4.37 Thermodynamic diagrams for carbon dioxide [1]: (A) Pressure-temperature diagram;
and (B) temperature-specific-entropy diagram.