Page 207 - Managing Global Warming
P. 207
Current and future nuclear power reactors and plants 169
4.4.2 Reactor coolants by type
4.4.2.1 Fluid coolants
Subcritical-pressure light water is the most “popular” reactor coolant. It will be used in
the subsequent comparisons as a reference case. In general, heavy water has many
thermophysical properties and behaviors that are quite close to those of light water
(for details, see Table 4.12). However, heavy water has a significantly lower neutron
capture cross-section compared to that of light water, which allows for more thorough
moderation. Therefore, only heat transfer characteristics of subcritical-pressure heavy
water will be compared with those of other coolants.
One of the advantages of light/heavy water is high heat-transfer coefficients at
forced convection and at flow boiling. However, there is a limit for efficient heat
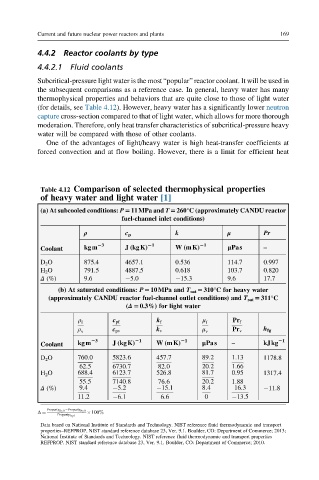
Table 4.12 Comparison of selected thermophysical properties
of heavy water and light water [1]
(a) At subcooled conditions: P511MPa and T5260°C (approximately CANDU reactor
fuel-channel inlet conditions)
ρ c p k μ Pr
23 21 21 –
kgm J (kgK) W(mK) μPas
Coolant
D 2 O 875.4 4657.1 0.536 114.7 0.997
H 2 O 791.5 4887.5 0.618 103.7 0.820
Δ (%) 9.6 5.0 15.3 9.6 17.7
(b) At saturated conditions: P510MPa and T sat 5310°C for heavy water
(approximately CANDU reactor fuel-channel outlet conditions) and T sat 5311°C
(Δ50.3%) for light water
ρ f c pf k f μ f Pr f
ρ v c pv k v μ v Pr v h fg
23 21 21 – 21
kgm J (kgK) W(mK) μPas kJkg
Coolant
D 2 O 760:0 5823:6 457:7 89:2 1:13 1178.8
62:5 6730:7 82:0 20:2 1:66
H 2 O 688:4 6123:7 526:8 81:7 0:95 1317.4
55:5 7140:8 76:6 20:2 1:88
Δ (%) 9:4 5:2 15:1 8:4 16:3 11.8
11:2 6:1 6:6 0 13:5
Property D 2 O Property H 2 O
Δ ¼ 100%
Property D 2 O
Data based on National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST reference fluid thermodynamic and transport
properties–REFPROP. NIST standard reference database 23, Ver. 9.1. Boulder, CO: Department of Commerce; 2013;
National Institute of Standards and Technology. NIST reference fluid thermodynamic and transport properties–
REFPROP. NIST standard reference database 23, Ver. 9.1. Boulder, CO: Department of Commerce; 2010.