Page 206 - Managing Global Warming
P. 206
168 Managing Global Warming
0.5 –266
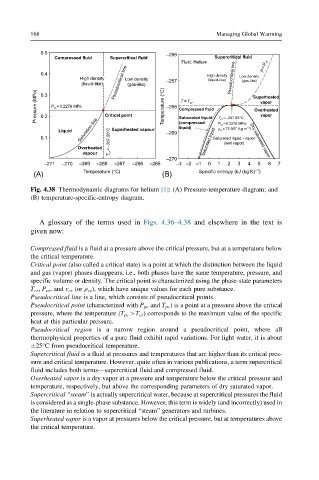
Compressed fluid Supercritical fluid Supercritical fluid
Fluid: Helium P=P cr
0.4 High density
High density Low density –267 (liquid-like) Pseudocritical line Low density
(gas-like)
(liquid-like) Pseudocritical line (gas-like)
Pressure (MPa) 0.3 P cr = 0.2276 MPa Critical point Temperature (°C) –268 Compressed fluid T cr = –267.95°C; Superheated
vapor
T=T cr
Overheated
vapor
0.2
Subcooled liquid
liquid)
Liquid Saturation line Superheated vapour –269 (compressed r cr = 72.567 (kg m –3 )
0.1 T cr =–267.95°C Saturated liquid Saturated liquid - vapor
Overheated (wet vapor)
vapour
P cr = 0.2276 MPa; Dry saturated vapor
–270
–271 –270 –269 –268 –267 –266 –265 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
–1
(A) Temperature (°C) (B) Specific entropy (kJ (kg K) )
Fig. 4.38 Thermodynamic diagrams for helium [1]: (A) Pressure-temperature diagram; and
(B) temperature-specific-entropy diagram.
A glossary of the terms used in Figs. 4.36–4.38 and elsewhere in the text is
given now:
Compressed fluid is a fluid at a pressure above the critical pressure, but at a temperature below
the critical temperature.
Critical point (also called a critical state) is a point at which the distinction between the liquid
and gas (vapor) phases disappears, i.e., both phases have the same temperature, pressure, and
specific volume or density. The critical point is characterized using the phase-state parameters
T cr , P cr , and v cr (or ρ cr ), which have unique values for each pure substance.
Pseudocritical line is a line, which consists of pseudocritical points.
Pseudocritical point (characterized with P pc and T pc ) is a point at a pressure above the critical
pressure, where the temperature (T pc >T cr ) corresponds to the maximum value of the specific
heat at this particular pressure.
Pseudocritical region is a narrow region around a pseudocritical point, where all
thermophysical properties of a pure fluid exhibit rapid variations. For light water, it is about
25°C from pseudocritical temperature.
Supercritical fluid is a fluid at pressures and temperatures that are higher than its critical pres-
sure and critical temperature. However, quite often in various publications, a term supercritical
fluid includes both terms—supercritical fluid and compressed fluid.
Overheated vapor is a dry vapor at a pressure and temperature below the critical pressure and
temperature, respectively, but above the corresponding parameters of dry saturated vapor.
Supercritical “steam” is actually supercritical water, because at supercritical pressures the fluid
is considered as a single-phase substance. However, this term is widely (and incorrectly) used in
the literature in relation to supercritical “steam” generators and turbines.
Superheated vapor is a vapor at pressures below the critical pressure, but at temperatures above
the critical temperature.