Page 141 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 141
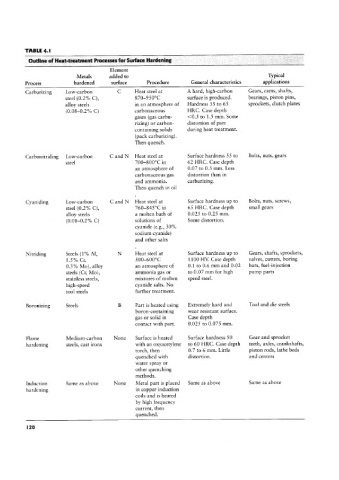
TABLE 4.l
Outline of Heat-treatment Processes for Surface Hardening
Element
Metals added to Typical
Process hardened surface Procedure General characteristics applications
Carburizing Low-carbon C Heat steel at A hard, high-carbon Gears, cams, shafts,
steel (0.2% C), 870-950°C surface is produced. bearings, piston pins,
alloy steels in an atmosphere of Hardness 55 to 65 sprockets, clutch plates
(0.08-0.2% C) carbonaceous HRC. Case depth
gases (gas carbu- <0.5 to 1.5 mm. Some
rizing) or carbon- distortion of part
containing solids during heat treatment.
(pack carburizing).
Then quench.
Carbonitriding Low-carbon C and N Heat steel at Surface hardness 55 to Bolts, nuts, gears
steel 700-800°C in 62 HRC. Case depth
an atmosphere of 0.07 to 0.5 mm. Less
carbonaceous gas distortion than in
and ammonia. carburizing.
Then quench in oil
Cyaniding Low-carbon C and N Heat steel at Surface hardness up to Bolts, nuts, screws,
steel (0.2% C), 760-845°C in 65 HRC. Case depth small gears
alloy steels a molten bath of 0.025 to 0.25 mm.
(0.08-0.2% C) solutions of Some distortion.
cyanide (e.g., 30%
sodium cyanide)
and other salts
Nitriding Steels (1% Al, N Heat steel at Surface hardness up to Gears, shafts, sprockets,
1.5% Cr, 500-600°C 1100 HV. Case depth valves, cutters, boring
0.3% Mo), alloy an atmosphere of 0.1 to 0.6 mm and 0.02 bars, fuel-injection
steels (Cr, Mo), ammonia gas or to 0.07 mm for high pump parts
stainless steels, mixtures of molten speed steel.
high-speed cyanide salts. No
tool steels further treatment.
Boronizing Steels B Part is heated using Extremely hard and Tool and die steels
boron-containing Wear resistant surface.
gas or solid in Case depth
contact with part. 0.025 to 0.075 mm.
Flame Medium-carbon None Surface is heated Surface hardness 50 Gear and sprocket
hardening steels, cast irons with an oxyacetylene to 60 HRC. Case depth teeth, axles, crankshafts
torch, then 0.7 to 6 mm. Little piston rods, lathe beds
quenched with distortion. and centers
Water spray or
other quenching
methods.
Induction Same as above None Metal part is placed Same as above Same as above
hardening in copper induction
coils and is heated
by high frequency
current, then
quenched.
|20