Page 337 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 337
- \\ 0 Introduction 3
Section 13 1
~e 1
Hot strip
Pickling and
Cold strip
oiling
1
i,}!‘\`!llu
\ ';:42':':`; X Irgél
Slab A Skelp >
Welded pipe
l
»»1i:u@!» ,
Steel plates
Plate
,Jw (4 *
el.;
_I
"`
Hot-rolled bars Cold-drawn bars ‘
Continuous I3 'l‘@ Q \ pup; H V,
~-_
casting or
A #if**> VY:-;§U;;Tg Wire
ingots p
Billet Rods '
Seamless pipe
Tube rounds
._ ,F Structural shapes
l'g§s&.
B'°°m -»»l§-ll»t!»ll~
Rails
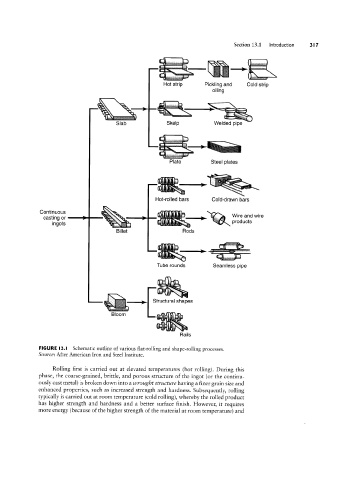
FIGURE I3.l Schematic outline of various flat-rolling and shape-rolling processes.
Source: After American Iron and Steel Institute.
Rolling first is carried out at elevated temperatures (hot rolling). During this
phase, the coarse-grained, brittle, and porous structure of the ingot (or the continu-
ously cast metal) is broken down into a wrought structure having a finer grain size and
enhanced properties, such as increased strength and hardness. Subsequently, rolling
typically is carried out at room temperature (cold rolling), whereby the rolled product
has higher strength and hardness and a better surface finish. However, it requires
more energy (because of the higher strength of the material at room temperature) and