Page 441 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 441
Section 16.11 Specialized Forming Processes
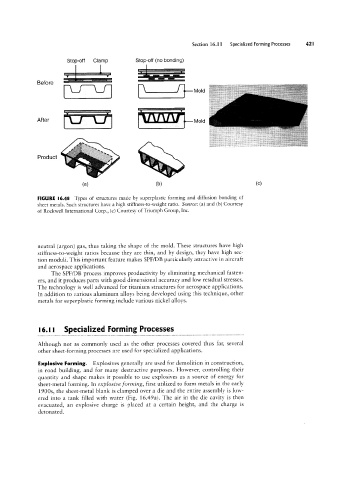
Stop-off Clamp Stop-off(no bonding)
Before
Mold
VVVVV
Product
P
(8) (D)
FIGURE |6.48 Types of structures made by superplastic forming and diffusion bonding of
sheet metals. Such structures have a high stiffness-to-weight ratio. Source: (a) and (b) Courtesy
of Rockwell International Corp., (c) Courtesy of Triumph Group, Inc.
neutral (argon) gas, thus taking the shape of the mold. These structures have high
stiffness-to-Weight ratios because they are thin, and by design, they have high sec-
tion moduli. This important feature makes SPF/DB particularly attractive in aircraft
and aerospace applications.
The SPF/DB process improves productivity by eliminating mechanical fasten-
ers, and it produces parts with good dimensional accuracy and lovv residual stresses.
The technology is Well advanced for titanium structures for aerospace applications.
In addition to various aluminum alloys being developed using this technique, other
metals for superplastic forming include various nickel alloys.
l6.ll Specialized Forming Processes
Although not as commonly used as the other processes covered thus far, several
other sheet-forming processes are used for specialized applications.
Explosive Forming. Explosives generally are used for demolition in construction,
in road building, and for many destructive purposes. However, controlling their
quantity and shape makes it possible to use explosives as a source of energy for
sheet-metal forming. In explosive forming, first utilized to form metals in the early
19005, the sheet-metal blank is clamped over a die and the entire assembly is low-
ered into a tank filled with Water (Fig. l6.49a). The air in the die cavity is then
evacuated, an explosive charge is placed at a certain height, and the charge is
detonated.